AAPM has contracted with NCRP to provide each AAPM Member in good standing access and download privileges of electronically available NCRP reports, commentaries and statements. This report was prepared by the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP). The Council strives to provide accurate, complete and useful information in its reports. However, neither the NCRP, the members of NCRP, other persons contributing to or assisting in the preparation of this report, nor any person acting on the behalf of any of these parties (a) makes any warranty or representation, express or implied, with respect to the accuracy, completeness or usefulness of the information contained in this report, or that the use of any information, method or process disclosed in this report may not infringe on privately owned rights; or (b) assumes any liability with respect to the use of, or for damages resulting from the use of, any information, method or process disclosed in this report.
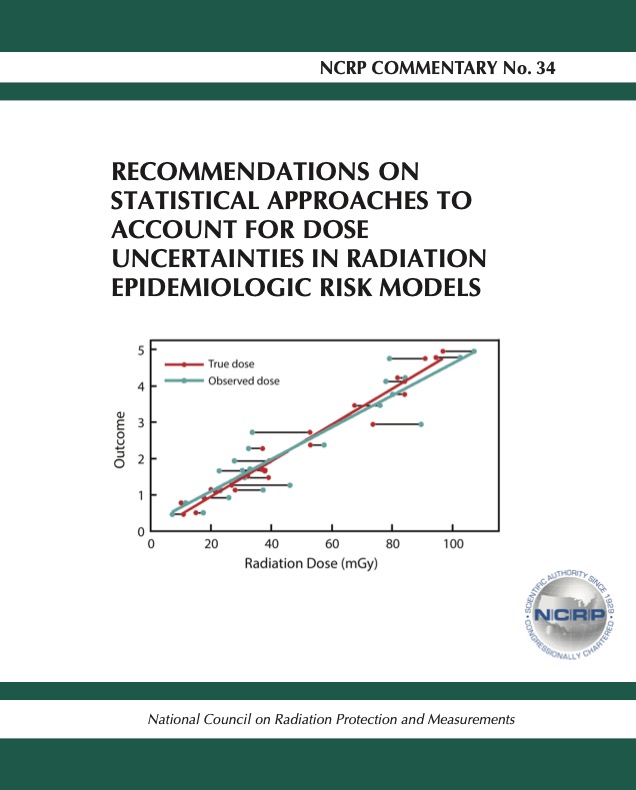 |
Commentary No. 034 - Recommendations on Statistical Approaches to Account for Dose Uncertainties in Radiation Epidemiologic Risk Models (2024) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Accurate exposure estimation in radiation epidemiologic studies is essential for reliable health risk assessment. Failure to account appropriately for uncertainties in dose estimation and model assumptions could lead to biased results in the evaluation of the radiation dose-response as well as incorrect confidence bounds for risk parameters. Assessment of absorbed dose is often subject to considerable uncertainties, and a variety of statistical approaches have been developed to incorporate dose uncertainties into the estimation and inference for the dose-response. The purpose of this Commentary is to provide a guide regarding available statistical methods for dose-response analysis that incorporate dose uncertainties, the types of studies to which the methods can be applied, and the advantages and disadvantages of the methods. This Commentary addresses studies of external and internal exposures and provides guidance on both shared and unshared uncertainty in the estimation of absorbed dose. Of particular interest are statistical methods for assessing dose-response in epidemiologic studies of internal emitters, for which doses are calculated using exposure and retention models with many parameters. Each parameter is associated with various sources and amounts of uncertainty. This Commentary draws from and builds upon previous National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) commentaries and reports on closely related topics, including:
This Commentary was prepared by Scientific Committee 1-28 on Recommendations on Statistical Approaches to Account for Dose Uncertainties in Radiation Epidemiologic Risk Models. Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Commentary No. 033 - Recommendations for Stratification of Equipment Use and Radiation Safety Training for Fluoroscopy (2023) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary In the practice of medicine, radiation safety training is necessary to protect both patients The purpose of this Commentary is to define an evidence-based, radiation-related classification for FGP based on patient radiation risk; to provide radiation-related recommendations for the types of fluoroscopes suitable for each class of procedure; and to indicate the extent and content of training that ought to be provided to different categories of facility staff who might enter a room where fluoroscopy is or may be performed. Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Commentary No. 032 - EVALUATION OF A SEX-SPECIFIC DIFFERENCE IN LUNG CANCER RADIATION RISK AND APPROACHES FOR IMPROVING LUNG CANCER RADIATION RISK PROJECTION (WITH A FOCUS ON APPLICATION TO SPACE ACTIVITIES) (2022) Price: $60 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary The study of Japanese atomic-bomb survivors exposed acutely to ionizing radiation in 1945 reported the risk of radiation-related lung cancer to be nearly three times greater for females than for males on a relative scale (similar for both mortality and incidence). The operational model for risk of exposure-induced death currently in use by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) relies on data from the Japanese atomic-bomb survivor study. According to the NASA model, radiation-related lung cancer is the largest contributor to fatal cancer risk. The sex-specific difference in lung cancer observed for Japanese atomic-bomb survivors is used in the model, resulting in a higher estimated total cancer mortality risk for female astronauts than for male astronauts for the same level of exposure. NASA requested that the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) evaluate the risk of radiation-related lung cancer in populations exposed to chronic (protracted or fractionated) radiation, in order to investigate whether a similar sex-specific difference in lung cancer risk is observed when exposure occurs gradually over years (such as experienced by astronauts during space missions) contrasted with the acute exposure received by the Japanese atomic-bomb survivors. Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Commentary No. 031 - Development of Kinetic and Anatomical Models for Brain Dosimetry for Internally Deposited Radionuclides (2022) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary This Commentary examines current information on the accumulation, distribution, and retention of radionuclides in the brain and the extent to which that information can be used to improve estimates of dose to potentially radiosensitive regions of the brain from internal emitters, with emphasis on high linear-energy transfer alpha particle-emitting radionuclides. Dose estimates for the brain based on explicit brain models reflecting best available biokinetic data are compared with estimates based on the brain models typically used in radiation protection and dose reconstruction. The comparisons indicate that predictions of brain doses based on current models for radionuclides may substantially underestimate or overestimate brain dose projections based on an explicit brain model reflecting best available biokinetic data. Potential improvements in dose estimates for the brain based on more detailed dosimetric models of the brain are also examined. Improved estimates of radiation doses to brain based on more realistic biokinetic and dosimetric representations of the brain would be an important step forward in ongoing epidemiologic research aimed at evaluating dementia, Alzheimerís, Parkinsonís, motor neuron diseases and cognitive impairment as possible adverse effects of radionuclide depositions in the brain. Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Commentary No. 030 - Using Personal Monitoring Data to Derive Organ Doses for Medical Radiation Workers, with a Focus on Lung (2020) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary The purpose of this Commentary is to describe an optimum approach for using personal monitoring data to estimate lung and other organ doses. The Commentary highlights specific precautions applicable to epidemiologic study of medical radiation workers. Such guidance is important as organ doses, along with associated epidemiologic analyses for both female and male populations, are necessary to assist the National Aeronautics and Space Administrationís (NASA) need to assess sex-specific lung cancer risks and radiation limits currently in place for female astronauts noting differences between the medical and space radiation environments. Overview available without login Scientific Committee:
|
 |
Commentary No. 029e - Naturally Occurring Radioactive Material (Norm) And Technologically Enhanced Norm (Tenorm) From The Oil And Gas Industry (2020) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary The presence of naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM) in the oil and gas indus- try has been known for over a century. NORM has existed since before our solar system was formed and includes uranium and thorium and their decay products. Because historic (con- ventional) drilling methods have met with dwindling oil and gas natural resources, newer technologies for oil and gas exploration and production have been developed and deployed. These newer technologies, termed unconventional oil and gas exploration and production, uti- lize hydraulic fracturing coupled with horizontal drilling. The operations associated with the newer technologies, and the wastes that are generated, differ from those associated with his- toric methods. They also create the potential for additional NORM and technologically enhanced NORM (TENORM) radiation exposures to workers and members of the public, envi- ronmental protection concerns, and waste management issues. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has the authority to regulate individual NORM radionuclides under the Clean Air Act (CAA), Clean Water Act (CWA), Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA), the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), the Toxic Sub- stances Control Act (TSCA), and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensa- tion, and Liability Act (CERCLA). While some NORM radionuclides are regulated under the CWA, CAA, and SDWA, EPA has not provided comprehensive regulations applicable to oil and gas exploration and production. As a result, regulation of radiation from NORM/TENORM falls to the states with minimal scientific recommendations from advisory bodies. Because of the lack of consistent regulations across the states, NORM/TENORM monitor- ing of workers and the workplace is inconsistent, and in many cases, rare or nonexistent. Clear guidance is needed to ensure that companies and regulatory agencies develop and implement defensible programs for radiation detection, NORM/TENORM measurements, and general radiation safety. Data from monitoring programs will help the oil and gas indus- try to fulfill its obligations under the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations (DOL 2020) that require classifying the potential hazards of chemicals, and com- municating information concerning hazards and appropriate protective measures to employ- ees. It will also enable comparison of potential radiation doses to workers and members of the public with dose criteria commonly used to protect public health. Lack of consistent, standard definitions of NORM and TENORM across state regulations and guidance documents often creates compliance difficulties. What remains nonexistent is a nationwide, consistent radiation protection framework for contemporary oil and gas TENORM. Lacking a federal or nationwide concentration limit, the Uranium Mill Tailings Radiation Control Act (UMTRCA) site release criteria have often been adapted as bulk-waste acceptance criteria. Applying an environmental remediation standard for free release of ura- nium mill tailings in surface soil as a waste landfill disposal limit may be overly restrictive as it seems to ignore the fact that landfills have engineered features and are located at suitable sites to limit environmental impacts. The radiation protection recommendations in National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) Report No. 180 (NCRP 2018) generally agree with International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) Publication 103 (ICRP 2007a). These recom- mendations address exposures of workers and the general public to above background levels of NORM/TENORM. A uniform basis for waste management decisions could be provided by appropriately developed performance-based waste disposal and site-remediation modeling, the definition of potential radiation exposure scenarios, and overall modeling considerations. NCRP formed a committee to conduct a scientific evaluation of the potential radiation protection and waste management issues from contemporary oil and gas exploration and produc- tion. Similarities and differences with the generation and disposal of NORM/TENORM waste or residuals from other activities beyond contemporary oil and gas production can be dis- cussed in a future NCRP report. The intended audience for this Commentary is the oil and gas industry stakeholders (i.e., industry management, states with oil and gas exploration and pro- duction, consultants, educators, and members of the public). The purpose of this Commentary is to:
An overview is available without charge to the public. Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Commentary No. 028 - Implementation Guidance for Emergency Response Dosimetry (2019) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 28 (2019) is a companion to National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements' (NCRP) Report No. 179 (2017), which defined the emergency worker and provided guidance to bridge the gap in managing dosimetry between trained, fully equipped emergency workers and the remainder community of responders during the early response period. Responders may arrive at the scene without appropriate dosimetry or radiation detection instrumentation and be expected to promptly measure and control radiation exposures while performing their functions, and later be assigned a radiation dose. This Commentary also complements NCRP Report No. 165 (NCRP 2010) and Commentary No. 19 (2005). Scientific Committee: |
 |
Commentary No. 027 - Implications of Recent Epidemiologic Studies for the Linear-Nonthreshold Model and Radiation Protection (2018) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 27 (2018) Implications of Recent Epidemiologic Studies for the Linear-Nonthreshold Model and Radiation Protection Historically, epidemiologic studies have assessed the health effects of ionizing radiation exposure from multiple sources: occupational, accidental, environmental, military and medical. The several national and international reviews in the last few decades of the health risks associated with exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation have generally agreed that human epidemiologic data on cancer induction observed at acute doses of 100 mGy and above are more reliable than those observed at <100 mGy, the low dose region. For the purpose of this Commentary, which focuses on low linear-energy transfer radiation, a low absorbed dose is <100 mGy delivered acutely, and a low absorbed-dose rate is <5 mGy h?1 for any accumulated dose. Scientific Committee: Roy E. Shore, Chair Lawrence T. Dauer, Co-Chair Harold L. Beck Emily A. Caffrey Scott Davis Helen A. Grogan Randall N. Hyer Fred A. Mettler, Jr. R. Julian Preston John E. Till Richrd Wakeford Linda Walsh Richard J. Vetter, Staff Consultant |
 |
Commentary No. 026 - Guidance on Radiation Dose Limits for the Lens of the Eye (2016) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary The National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP), with financial support from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission, addresses radiation protection principles with respect to the lens of the eye, summarizes the current understanding of eye biology and lens effects (including ionizing radiation effects), reviews and evaluates the current epidemiology related to ionizing radiation and cataracts, assesses exposed populations with the potential for significant radiation exposures to the lens, and makes conclusions and recommendations. Commentary No. 26, Guidance on Radiation Dose Limits for the Lens of the Eye, takes into account the most current information regarding the epidemiologic and mechanistic understanding of the development of cataracts and specifically addresses four core questions:
EA Blakely, Co-Chair LT Dauer, Co-Chair EA Ainsbury JR Dynlacht DG Hoel BEK Klein DM Mayer CR Prescott RH Thornton E Vano GE Woloschak Consultants CM Flannery LE Goldstein N Hamada PK Tran |
 |
Commentary No. 025 - Potential for Central Nervous System Effects from Radiation Exposure During Space Activities Phase I: Overview (2016) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 25 (2016) Potential for Central Nervous System Effects from Radiation Exposure During Space Activities Phase I: Overview Scientific Committee: Leslie A. Braby, Co-Chair Richard S. Nowakowski, Co-Chair Gregory T. Armstrong Lee E. Goldstein Kathryn D. Held Gregory A. Nelson James C. Root Walter Schimmerling Rudolph E. Tanzi Lawrence W. Townsend, Consultant |
 |
Commentary No. 024 - Health Effects of Low Doses of Radiation: Perspectives on Integrating Radiation Biology and Epidemiology (2015) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 24 (2015) provides general perspectives on the integration of results of basic science studies, including biomarkers and bioindicators of cancer and other diseases, with epidemiologic studies on health effects of low doses of radiation. Scientific Committee: Sally Amundson, Co-Chair Jonine Bernstein, Co-Chair John Boice Raymond Guilmette Amy Kronenberg Mark Little William Morgan Jac Nickoloff Simon Powell Daniel Stram R. Julian Preston, Consultant |
 |
Commentary No. 023 - Radiation Protection for Space Activities: Supplement to Previous Recommendations (2014) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Scientific Committee: Dudley Goodhead, Co-Chairman R. Julian Preston, Co-Chairman Patricia A. Fleming Kathryn D. Held Amy Kronenberg Gregory A. Nelson Walter Schimmerling Roger P. Shaw Michael M. Weil |
 |
Commentary No. 022 - Radiological Health Protection Issues Associated With Use of Active Detection Technology Systems for Detection of Radioactive Threat Materials (2011) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary NCRP Commentary No. 22: -examines the potential radiation doses from ADT systems to operating personnel, bystanders, and other individuals in the inspected areas; and design and operational factors that must be considered in assessing the safety and efficiency of ADT systems. -provides recommendations on the research, development and fielding of ADT systems under consideration by DTRA to optimize the effective and safe use of these systems; address the full range of safety and health concerns associated with the deployment of ionizing radiation systems that currently exist, are under development, or may be developed in the future for the detection and interdiction of weapons of mass destruction SNM devices that could be used in acts of terrorism. -endorses the recommendations and analyses of Commentary No. 21 (2011) of the issues of importance in the development and deployment of security systems involving ionizing radiation. -provides recommendations related to radiation protection design considerations, engineering controls, and operational practices and procedures for the various ADT systems that are being evaluated by DTRA and its contractors. The technologies under consideration for ADT systems will employ radiation sources for detection of SNM and other radiological materials of possible use in weapons of mass destruction. It is planned for these active detection systems to be deployable at standoff ranges or in shielded configurations. Scientific Committee: John F. Ahearne, Chairman Lawrence T. Dauer Christine A. Donahue Norman C. Fost Helen A. Grogan Daniel F. Kassiday James C. Liu Kathryn H. Pryor Scottie W. Walker Glen I. Reeves, Consultant S. James Adelstein, Advisor |
 |
Commentary No. 021 - Radiation Protection in the Application of Active Detection Technologies (2011) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary The U.S. government is actively pursuing efforts to develop, acquire and support the deployment of enhanced detection systems for special nuclear material (SNM). While the Domestic Nuclear Detection Office in the U.S. Department of Homeland Security is the lead agency in this area, both the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA) in the U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) support programs to develop and field an active detection technology (ADT) system. This Commentary focuses on the efforts of DTRA to deploy a detection system that addresses their mission. It is intended as guidance to inform the development process with respect to radiation protection issues. The comments and recommendations in this Commentary are broadly applicable to all ADTs used to detect SNM. Subsequent reports are planned that will cover more technical details regarding implementation of the guidelines in this Commentary. This Commentary reviews the new remote detection technologies that are being developed, focusing on the requirements for radiation protection and provides guidelines to ensure that doses are within recommended limits for operating personnel and bystanders in the inspected areas. Scientific Committee: Kenneth L. Miller, Chairman Debbie B. Gilley, Vice Chairman J. Donald Cossairt Thomas A. Cotton David M. Hassenzahl Joseph M. Kaminski Sayed H. Rokni Scott O. Schwahn Norman Fost, Consultant Glen Reeves, Consultant |
 |
Commentary No. 020 - Radiation Protection and Measurement Issues Related to Cargo Scanning with Accelerator-Produced High-Energy X Rays (2007) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary The Domestic Nuclear Detection Office of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) requested that NCRP provide specific radiation protection advice relevant to the Cargo Advanced Automated Radiography System (CAARS) currently under development. CAARS is designed to detect high atomic number (Z > 72) material which might be special nuclear material or shielding designed to conceal radioactive material. In addition, it must have a conventional radiographic imaging capability to detect illicit drugs, high explosives, and other contraband (e.g., weapons, currency) in cargo conveyances. This Commentary: - recommends a dose limit for individuals who might be inadvertently exposed to radiation in a conveyance within the CAARS exclusion zone; and also: - addresses the methods for estimating by calculation and verifying by measurement such doses delivered by CAARS; - discusses the estimated change in health risk to such an individual as a function of dose; - recommends various methods for ensuring the dose limit to an inadvertentlyexposed individual is not exceeded; - describes the physical properties of the interaction between high-energy radiation and material that influence both the doses delivered and the methods for measuring such doses; and - recommends specific methods for measuring the maximum dose to an exposed individual in a scanned conveyance. - addresses the maximum cumulative effective dose in an hour to an individual working outside the exclusion zone of a CAARS facility; and also: - recommends system features and operational procedures to ensure that worker doses remain as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA); and - recommends specific methods for measuring dose to an individual working outside the exclusion zone. - recommends an administrative control for annual effective dose to members of the public outside the perimeter of a CAARS facility. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-95-6 View the latest Book Review of this Commentary. Scientific Committee: Leslie A. Braby, Chairman Paul M. Bergstrom Richard R. Brey Christine A. Donahue Michael P. Grissom Timothy J. Jorgensen Richard T. Kouzes James C. Liu Michael A.S. Taylor, Sr. Ralph H. Thomas, Advisor |
 |
Commentary No. 019 - Key Elements of Preparing Emergency Responders for Nuclear and Radiological Terrorism (2005) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary This Commentary has been prepared at the request of the US Department of Homeland Security (DHS). The recommendations in the Commentary are intended for officials of DHS and state and local authorities who prepare emergency responders for terrorist incidents that involve radiation or radioactive materials. These incidents could result from use by terrorists of a radiation exposure device, a radiological dispersal device, or an improvised (or otherwise obtained) nuclear device. This Commentary is limited to the key elements of preparing emergency responders for nuclear and radiological terrorism and focuses on: - equipment requirements for emergency responders, including radiation detection and personal protection equipment for different types and levels of radiation; - radiation decontamination advice and equipment, and medical supplies needed at the local level; and - the content and frequency of training and exercises for emergency responders at the federal, state and local levels (i.e., with regard to radiation protection aspects). ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-88-8 Scientific Committee:: John W. Poston Sr., Chairman Twenty two expert members from academia, government agencies and the private sector. |
 |
Commentary No. 018 - Biological Effects of Modulated Radiofrequency Fields (2003) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 18 (2003) examines the literature on biological effects of exposure to modulated radiofrequency (RF) energy to determine whether present exposure standards and guidelines need to be modified further to take modulation into account. Modulation occurs in a wide variety of forms specialized for radar, wireless communications, broadcast communications, and industrial processes with the result that many waveforms, pulse widths, spectral properties, and temporal patterns need consideration. In pulse modulation the RF energy is rapidly switched on and off, whereas amplitude modulation produces a continually changing level of RF energy. Frequency-modulated RF energy has signal amplitudes that remain essentially constant, but vary in frequency within some narrowly prescribed range and more closely resembles nonmodulated RF energy than pulsed or amplitude modulated RF fields. For radar, pulses generally have durations measured in fractions of a microsecond to a few microseconds. Intervals between pulses (or pulse groups) are considerably longer resulting in low duty cycle, that is, RF energy is on for a small fraction of time during each period. But pulsed signals used for communications systems can have durations in the range of milliseconds, higher duty cycles, and additional modulation features. Specialized military systems constitute a subcategory with very intense, brief pulses. The literature related to modulation-dependent effects of RF energy is a small part of the total scientific literature with relatively few experimental studies of animals that were designed to examine biological effects of electromagnetic fields as a function of modulation. However, several dozen studies in the literature were designed to permit a comparison of biological effects of pulsed versus continuous-wave RF energy in the same species. Only a few of these studies made similar direct examinations of biological effects of amplitude modulation at extremely low frequency and there are very few long-term animal studies that directly address health concerns for exposures to RF energy that is sinusoidally amplitude modulated. The results are mixed, but suggest that pulsed RF energy can be more effective in producing biological effects under some circumstances than continuous wave energy of the same average incident power density. Some questions concerning extremely low frequency amplitude modulation also remain unanswered. Most studies of pulsed RF energy involved exposures consisting of short (microsecond) pulses of comparatively high intensity, and time-averaged exposure levels that are considerably above the contemporary exposure limits. These studies do not suggest a hazard that might be present under exposure conditions allowed by the current limits. There is some evidence, both theoretical and experimental, that very intense RF pulses, which increase the temperature of tissue by several degrees within a second, can lead to adverse effects through a mechanism that relates to the rate of heating. Exposures to such pulses are, in principle, permissible under some contemporary exposure guidelines. However, such exposures are associated with specialized military weapon systems. Human beings are very unlikely to experience inadvertent exposures to such intense pulsed RF energy. Some animal studies have reported biological effects of RF energy modulated sinusoidally or by long- or short-duration pulses, sometimes at low average power levels. Unfortunately, the research on animals and cell and tissue systems exposed under these conditions is sparse and scattered over a variety of waveforms, experimental designs, animal species, and reported biological effects. Most reports have no clear relation to possible health hazards and do not suggest possible hazards from modulated RF energy at levels below present limits. A few other studies fail to demonstrate health hazards, but raise questions that are the subject of current research. Biophysical considerations do not suggest a plausible basis for hazards from electromagnetic fields at exposure levels below present limits that are associated with modulation, with the possible exception of very intense RF pulses. This Commentary concludes that the scientific literature related to modulation-dependence of biological effects of RF energy is not sufficient to draw any conclusions about possible modulation-dependent health hazards of RF fields, nor is there any apparent biophysical basis from which to anticipate such hazards apart from exposure to very intense RF pulses produced by some specialized military equipment. Scientific Committee: Om P. Gandhi, Chairman John D'Andrea Kenneth R. Foster Arthur W. Guy Don R. Justesen Indira Nair Asher R. Sheppard |
 |
Commentary No. 017 - Pulsed Fast Neutron Analysis System Used in Security Surveillance (2003) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 17 (2003) is a compilation of responses to three separate issues concerning the PFNA system. The first response was completed in September 2002, entitled Radiation Protection Advice for Pulsed Fast Neutron Analysis System Used in Security Surveillance. It covers: (1) the appropriate dose limit for persons inadvertently irradiated by the PFNA system, (2) the proper methods to determine the dose received, and (3) an opinion on whether the use of the PFNA system could result in levels of activation products in pharmaceuticals and medical devices that might be of concern to public health. The second response was completed in February 2003, entitled Radiation Protection Advice for the Pulsed Fast Neutron System Used in Security Surveillance: Part II. The ALARA Principle and Related Issues. It covers: (1) a description of the relevant concepts of radiation protection that should be applied to the PFNA system; (2) a critique, in the form of advice on the necessary content of the draft System Safety Specifications and the draft Radiation Safety Plan for the PFNA system; and (3) the application of the ALARA principle to the PFNA system. The third response was completed in July 2003, entitled Radiation Protection Advice for the Pulsed Fast Neutron System Used in Security Surveillance: Part III. Methods for the Determination of Effective Dose to Inadvertently Exposed Individuals. It covers the specific methods and instruments recommended for the measurement of and the determination of the radiation dose (i.e., the effective dose) that an individual would receive by inadvertent exposure to radiation from the PFNA system. Scientific Committee: Leslie A. Braby, Chairman David M. Gilliam Lawrence R. Greenwood Charles B. Meinhold Susan D. Wiltshire Bruce L. Freeman, Consultant |
 |
Commentary No. 016 - Screening of Humans for Security Purposes Using Ionizing Radiation Scanning Systems (2003) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 16 (2003) presents radiation protection advice concerning ionizing radiation-producing devices that are being evaluated for various uses in screening of humans for the purpose of security. Chief among the devices being evaluated at the present time are scanning systems that utilize x rays. This Commentary primarily addresses systems utilizing ionizing radiation, but also describes briefly some systems under consideration that utilize nonionizing radiation. Scientific Committee: Kenneth L. Miller, Chairman David J. Brenner Frank Cerra Joel O. Lubenau R. Julian Preston |
 |
Commentary No. 015 - Evaluating the Reliability of Biokinetic and Dosimetric Models and Parameters Used to Assess Individual Doses for Risk Assessment Purposes (1998) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 15 (1998) addresses in considerable detail the uncertainties associated with models used in radiation protection for: (1) the gastrointestinal tract, (2) the respiratory tract, (3) the skin, (4) internal biokinetics, (5) dosimetry of internally deposited radionuclides, and (6) estimation of radiation doses attributable to radionuclides in the environment. Sections on the reliability of dose coefficients for estimation of individual risk and a summary are also included. Scientific Committee:: Andre Bouville, Chairman Keith F. Eckerman William C. Griffith F. Owen Hoffman Richard W. Leggett James Stubbs |
 |
Commentary No. 014 - A Guide for Uncertainty Analysis in Dose and Risk Assessments Related to Environmental Contamination (1996) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 14 (1996) addresses key issues involved in performing and reviewing quantitative uncertainty analyses. The Commentary emphasizes the importance of rigorously defining the assessment endpoint, the need for expert judgement in the absence of relevant data sets, and the use of uncertainty analysis in an iterative mode to define model components warranting more detailed investigation. Guidance is given on when and how to perform an uncertainty analysis, and how to use formal elicitation of expert judgement in the absence of site-specific data to obtain the most defensible quantification of the current state of knowledge about critical parameters and model components. The Commentary constitutes an element in the Council's overall effort focused on uncertainty in environmental dose calculations and associated risks. Previously, the NCRP released Commentary No. 8, Uncertainty in NCRP Screening Models Relating to Atmospheric Transport, Deposition and Uptake by Humans, and other studies are underway that are concerned with (1) uncertainties in the application of metabolic models and (2) uncertainties in fatal cancer risk estimates used in radiation protection. Scientific Committee: F. Owen Hoffman, Chairman David E. Burmaster William J. Conover Richard O. Gilbert Eduard Hofer Stephen C. Hora Ronald G. Whitfield |
 |
Commentary No. 013 - An Introduction to Efficacy in Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (Justification of Medical Radiation Exposure) (1995) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 13 (1995) discusses the concept of efficacy as it applies to the use of radiation in diagnostic radiology and nuclear medicine and describes the interrelationships of efficacy with cost-effectiveness and cost-benefit analysis, including consideration of potential radiation detriment, as well as with outcome research and technology assessment. Inherent in the decision to use radiation as a tool in diagnosis is the understanding that every radiation exposure needs to be justified. Since it is only through the development of medical decision-making concepts such as efficacy that decisions concerning justification can be made, NCRP finds the evaluation of radiation exposure involved in a practice or procedure an essential part of evaluating efficacy. The Commentary presents a general hierarchical model to classify efficacy studies. This hierarchy extends from basic laws of physics, through clinical use, to more general patient outcome and societal issues. Discussion of this hierarchy is followed by a discussion of the applications of efficacy concepts to the assessment and emergence of a new technology. Next, the relations of outcome research, technology assessment, and efficacy are explored. The final section summarizes the logical relationships of efficacy levels and the use of imaging efficacy concepts in clinical decision making. Scientific Committee: John R. Thornbury, Chairman Dennis G. Fryback Robert A. Goepp Lee B. Lusted (deceased) Keith I. Marton Barbara J. McNeil Charles E. Metz Milton C. Weinstein |
 |
Commentary No. 012 - Radiation Exposure and High-Altitude Flight (1995) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 12 (1995) explores radiation protection considerations associated with high-altitude flight at an altitude of 65,000 feet (20,000 m) or so. It addresses relevant considerations such as dose rates at different altitudes, dose rates from solar flares, biological effects of ionizing radiation at these altitudes, and the associated radiation risk estimates. Estimates of radiation risk for flight crew, passengers, frequent travelers, and conventional travelers are made. The Commentary concludes with comments on aspects of radiation protection philosophy and measurements that need to be addressed to operate commercial aircraft at these altitudes. Scientific Committee: Warren K. Sinclair, Chairman Leslie A. Braby R. J. Michael Fry Charles B. Meinhold, Advisor |
 |
Commentary No. 011 - Dose Limits for Individuals Who Receive Exposure from Radionuclide Therapy Patients (1995) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 11 (1995) is a result of concern about the exposure of family members of recently discharged radionuclide therapy patients. This subject was last addressed in NCRP Report No. 37 entitled, Precautions in the Management of Patients Who Have Received Therapeutic Amounts of Radionuclides, which was published in 1972. Family members of radionuclide therapy patients would usually be considered members of the public and, therefore, would normally be limited to 1 mSv annually. However, because of the infrequent nature of the exposure and because of the benefits that accrue to a family from a patient's radiation therapy. Commentary No. 11 considers it acceptable for family members of such patients to accrue up to 5 mSv annually and that there may be specific instances when the patient's physician would allow a member of the patient's family to receive an exposure of up to 50 mSv annually. In cases when such an exposure is anticipated, training and individual monitoring should be provided. In the Commentary, there is a discussion of the different types of therapy that can be provided and of the potential exposure from each therapeutic modality. Material in an appendix provides examples of the various situations that can occur. Ultimately, the material in the Commentary is to be included in the revision on NCRP Report No. 37 which is now underway. Scientific Committee: Anthony R. Benedetto, Chairman James E. Carey Harold Dworkin Richard G. Lane |
 |
Commentary No. 010 - Advising the Public About Radiation Emergencies (1994) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 10 (1994) was given the subtitle, "A Document for Public Comment," to reflect the desire of NCRP to begin a dialogue on what information and what form of presentation can prove helpful to members of the public in assessing emergency situations with potential for radiation exposure. This is based on the Council's belief that the bedrock foundation of any plan to protect the public from radiation effects, particularly in time of emergency, is reliable information presented to an informed public. This Commentary presents suggestions for informing the public about radiation and about emergencies that involve radiation. Treated are information sources, perceptions and the need for credibility. Also provided in the Commentary is discussion of what information can prove valuable in a radiation emergency and, importantly, a proposed radiation index (i.e., a numerical scale for comparison of various radiation exposures). The Council particularly seeks reaction to the proposed index. Scientific Committee: M. Carl Bell, Chairman Clayton S. French James A. Grundl Bernd Kahn Eugene L. Saenger |
 |
Commentary No. 009 - Considerations Regarding the Unintended Radiation Exposure of the Embryo, Fetus or Nursing Child (1994) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 9 (1994) seeks to (1) draw special attention to the problems in protection of the embryo, fetus and nursing child that might result from the use of radiation in the medical diagnosis and treatment of the mother, and (2) assist the Nuclear Regulatory Commission in developing requirements appropriate to dealing with the unintended exposure of the embryo, fetus or nursing child as a result of such procedures. The Commentary highlights the fact that physicians must be constantly alert for the patient who may be pregnant or breast feeding. Commentary No. 9 summarizes the doses to the embryo, fetus or nursing child that might result from radiological procedures, brachytherapy to the mother, teletherapy to the mother, and the administration of radiopharmaceuticals to the mother. The Commentary then goes on to treat the risks attributable to these radiation exposures including those for deterministic effects and stochastic effects. Finally, the Commentary sets out recommendations and conclusions aimed at the specification of requirements for action after radiation exposure of the embryo, fetus or nursing child. Scientific Committee: Warren K. Sinclair, Chairman S. James Adelstein Robert L. Brent Richard L. LaFontaine, Consultant |
 |
Commentary No. 008 - Uncertainty in NCRP Screening Models Relating to Atmospheric Transport, Deposition and Uptake by Humans (1993) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 8 is related to Commentary No. 3, Screening Techniques for Determining Compliance with Environmental Standards. That document presented screening models and parameter values for assessing potential releases of small quantities of radionuclides to the atmosphere, models that will also be included in a forthcoming report that covers other pathways as well. Commentary No. 8 evaluates the reliability of these screening models and identifies situations where the use of the models and parameter values needs to be restricted or modified prior to application. The primary assumptions affecting bias in the models are also reviewed in Commentary No 8. Major sections of the Commentary treat atmospheric transport and deposition, food chain transport, human dietary habits and usage factor, and external and internal dose factors. Scientific Committee: F. Owen Hoffman, Chairman Andre Bouville Steven R. Hanna Charles W. Miller F. Ward Whicker B. Gordon Blaylock, Consultant |
 |
Commentary No. 007 - Misadministration of Radioactive Material in Medicine? Scientific Background (1991) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 7 (1991) is concerned with an assessment of the effects of various levels of radiation exposure that might result from what have been denominated as misadministration of radiopharmaceuticals. Practitioners in the nuclear medicine field and the Nuclear Regulatory Commission have been concerned about proposed reporting requirements for misadministrations. The Commentary provides information on effects that might result from various levels of exposure. Commentary No. 7 is intended to provide a scientific basis for consideration of nuclear medicine misadministrations. Major sections of the Commentary treat the quantity of radioactive materials routinely administered in nuclear medicine procedures, frequency of misadministrations in nuclear medicine and expected radiobiological effects -- deterministic and stochastic. Scientific Committee: Warren K. Sinclair, Chairman A. Bertrand Brill James G. Kereiakes Clarence C. Lushbaugh James S. Robertson Fun Fong, Jr., Advisor |
 |
Commentary No. 006 - Radon Exposure of the U.S. Population? Status of the Problem (1991) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 6 (1991) reviews the present state of knowledge and consolidates, in a succinct form, information and guidance on radon. Addressed are the status of epidemiology studies and estimated health risks. The document leaves unchanged the Council's 1984 recommendation on a remedial action level but recognizes the need for further review utilizing the results of studies currently underway. NCRP has long been concerned about the potential effects of radon exposure and previously published NCRP reports treating this subject made evident the view that radon exposure constitutes the most important potential public health hazard attributable to radiation in the United States today. NCRP: Warren K. Sinclair, President |
 |
Commentary No. 005 - Review of the Publication, Living Without Landfills (1989) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 5 (1989) provides a review of the report Living Without Landfills, which was published by the Radioactive Waste Campaign. The subject of radioactive waste management was deemed to involve such important questions of public policy that the Council determined to deviate from previous practice and, in response to a request, agreed for the first time to review a document prepared by another organization. This Commentary should represent an important contribution to the public interest in that it is intended to constitute an objective scientific input in to the increasingly strident public dialogue about radioactive waste. After a brief introduction, the Commentary treats such matters as the exclusion of relevant information, misstatement of facts, examples of exaggeration and bias, and examples of faulty logic. Scientific Committee: Merrill Eisenbud, Chairman Roger W. Granlund William R. Hendee Frank L. Parker Paul Slovic |
 |
Commentary No. 004 - Guidelines for the Release of Waste Water from Nuclear Facilities with Special Reference to the Public Health Significance of the Proposed Release of Treated Waste Waters at Three Mile Island (1987) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Commentary Commentary No. 4 (1987) is an addition to the series of documents that provide preliminary evaluations, exploratory studies or extensions of previously published NCRP reports. Commentary No. 4 represents the Council's response to the Nuclear Regulatory Commission's call for comments on proposals for disposal of waste water at the Three Mile Island (TMI) nuclear power plant. While the Commentary focuses on the Three Mile Island situation, some aspects have a generic character. Treated in the Commentary are the status of accident generated waste water at TMI; options for the treatment of tritiated waste waters; tritium?physical and chemical properties, environmental transport, and pathways of exposure; dosimetry; dose equivalents resulting from release of tritiated waste water to the atmosphere and surface water; and potential health effects. Scientific Committee: Frank L. Parker, Chairman A. Bertrand Brill Donald G. Jacobs Bernd Kahn Edward Watson |
 |
Report No. 187 - Operational Radiation Safety Program (2022) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report discusses the basic principles for establishing and maintaining an effective operational radiation safety program. It is intended for individuals with responsibility for these programs and assumes some level of formal education, training, and experience in radiation safety. Overview available without login Scientific Committee: Kathryn H. Pryor, Chair, Edgar D. Bailey, Christine A. Donahue, Eric M. Golden, Barbara L. Hamrick, Willie O. Harris, Michael Lewandowski, Michael L. Littleton, David S. Myers, John W. Poston, Debra M. Scroggs, Kathleen L. Shingleton, Glenn M. Sturchio, Joshua Walkowicz, James S. Willison, James G. Yusko, Elizabeth M. Brackett, Advisor, Frazier Bronson, Advisor, J. Donald Cossairt, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 186 - Approaches for Integrating
Information from Radiation
Biology and Epidemiology
to Enhance Low-Dose
Health Risk Assessment (2020) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The overall aim of this Report is to provide input for the development of biologically based dose-response models for radiation-induced cancers and circulatory disease that use an adverse outcome pathways and key-events approach for providing parameters for these models. These mechanistic data can be integrated with the most recent epidemiologic data to develop overall dose response curves for radiation-induced adverse health outcomes. This integration of the findings from radiation biology and epidemiology will enhance the risk assessment process by reducing uncertainties in estimated risk following exposure to low doses and low dose rates of ionizing radiation. Overview available without login Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Report No. 185 - Evaluating and Communicating Radiation Risks for
Studies Involving Human Subjects: Guidance for Researchers
and Institutional Review Boards (2020) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The extent of knowledge about ionizing radiation in general, radiation involved in medical procedures, and the potential adverse effects of radiation varies substantially among members of the public and within the medical community. Also, although many U.S. academic institutions provide guidelines for the conduct of human research, including research involving radiation, these guidelines lack uniformity. There is a need to provide comprehensive, consistent and accurate guidance on radiation risks of research protocols that involve the use of ionizing radiation to those who develop protocols and conduct research involving human subjects and to institutional review boards (IRBs) that review these protocols. This Report seeks to fill these gaps by: Overview available without login
|
 |
Report No. 184 - Medical Radiation Exposure of Patients in the United States (2019) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report is an update of NCRP Report No. 160, Ionizing Radiation Exposure of the Population of the United States, Section 4 (Medical Exposure of Patients) (2009). This Report evaluates average individual effective dose and collective effective doses from medical exposures for the 2016 timeframe. The Report pays particular attention to those procedures that contribute the largest share and provides information on nominal effective dose values that individual patients may experience from a specific examination. It is very important to note that these effective dose values should not be used as an indication of acceptability or to estimate individual cancer risk from a certain radiation procedure, but rather used as a metric to broadly compare the magnitude of potential stochastic effects to populations from different radiation sources. This Report does not quantify associated health risks nor discuss potential medical benefits. The Report also does not specify any actions that should be taken in light of these latest data. These subjects were outside the scope of the charge to NCRP. The Report is aimed at medical professionals, patients, regulators, and those involved in radiation protection. It provides indices for comparison among radiation sources and at different time periods. Overview available without login
|
 |
Report No. 183 - Radiation Exposure in Space and the Potential for Central Nervous System Effects: Phase II (2019) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report has been prepared at the request of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). It is the second phase of a two-phase effort intended to provide guidance to NASA concerning the health effects and mission impacts of space radiation exposure on the central nervous system (CNS) of crew members. The first phase of effort resulted in the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) Commentary No. 25, Potential for Central Nervous System Effects from Radiation Exposure During Space Activities. Phase I: Overview, which described the critical issues surrounding the potential short- and long-term consequences of space radiation on the CNS and laid the groundwork for a more comprehensive investigation that is the basis of this Report. This Report summarizes the steps and approaches needed to more fully understand the risk of CNS effects following radiation exposures in space and provides guidance for radiation protection, including risk management. NCRP has identified knowledge gaps regarding the implementation of a comprehensive and effective radiation safety program to protect astronauts against the potential for early and late CNS effects from space radiation. Overview available without login
|
 |
Report No. 182 - Radiation Safety of Sealed Radioactive Sources (2019) Price: $70 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report provides information on the safe design, acquisition, use and disposition of sealed radioactive sources from "cradle to grave" in a variety of occupational settings. The essential elements of a comprehensive sealed radioactive source program are of interest to operational radiation safety professionals, regulatory authorities, and users of sealed radioactive sources. Sort Title : Report No. 182 ISBN : 9781944888084 Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Report No. 181 - Evaluation of the Relative Effectiveness of Low-Energy Photons and Electrons in Inducing Cancer in Humans (2018) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report draws on an evaluation by specialists in microdosimetry, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) damage, cellular radiobiology, animal studies, and human epidemiology of the available evidence in those fields of study relevant to estimation of the relative effectiveness of lower-energy photons and electrons in inducing cancer in humans. For each specialty area (line of evidence), probability density functions (PDFs) are derived for the biological effectiveness observed for the endpoints studied in each line of evidence for defined lower-energy groups. Using these PDFs and evaluation of the relevance of the data from each line of evidence to the risk of cancer in humans, an evaluation is then made of the relative effectiveness of the defined lower-energy groups of photons or electrons (compared with higher-energy photons or electrons) in inducing cancer in humans. Overview available without login Scientific Committee: S.L. Simon, Chair L.A. Braby P.Y. Chang D.T. Goodhead S.C. Hora K. Mabuchi J.S. Puskin D.B. Richardson J.D. Tucker Consultants: K.F. Eckerman D.C. Kocher E. Vano |
 |
Report No. 180 - Management of Exposure to Ionizing Radiation: Radiation Protection Guidance for the United States (2018) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Since NCRP Report No. 116 was published in 1993, there have been advances in knowledge regarding the biological effects of ionizing radiation, particularly relating to cancer. In addition, health effects other than cancer such as cardiovascular disease and cataracts are emerging as potentially important concerns. A discussion of established ethical principles and their application to radiation protection had not been introduced in NCRP Report No. 116. Furthermore, the Fukushima nuclear reactor accident and the potential for a nuclear or radiological incident in the United States, as well as the increase in population exposure to medical use of ionizing radiation (particularly computed tomography examinations, positron emission tomography scans, and nuclear medicine procedures) have increased the awareness of the importance of radiation protection guidance in the United States. In 2007, the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) published revised recommendations for its system of radiological protection (ICRP Publication 103). Subsequently an important ICRP report on tissue reactions (also called deterministic effects), including early and late effects (ICRP Publication 118), was published in 2012. While the goals for radiation protection in the United States are the same as those for the international community, there are some differences in the specific approaches taken to achieve these goals. NCRP radiation protection principles for exposure of humans are now expressed as: justification, optimization of protection, and numeric protection criteria (for management of dose to an individual). When there is a numeric protection criterion for a specific exposure situation, the first objective is to meet that protection criterion, then optimization of protection should be applied. These differences are discussed in this Report. Overview available without login Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Report No. 179 - Guidance for Emergency Response Dosimetry Recommendations of the NATIONAL COUNCIL ON RADIATION PROTECTION AND MEASUREMENTS (2017) Price: $85 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Executive Summary: National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) Report No. 179, Guidance for Emergency Response Dosmetry, complements three previous NCRP publications that provide advice on planning responses to radiological or nuclear terrorism incidents. The Report provides guidance on the accrual and control of radiation dose in the emergency phase of a radiological or nuclear incident and answers three questions: - With minimal dosimetry resources, how do responders make decisions to control the total dose and associated risk? - How are doses assigned to responders when not every responder is issued a dosimeter before exposure occurs? - What is the regulatory framework for responders who are not trained as radiation workers? The Report guidance bridges the gap between trained and equipped emergency workers and the remainder community of responders. Emergency workers are defined as those workers who would be called to assist with the response to a radiological or nuclear incident, acknowledging that most emergency workers have jobs that do not routinely expose them to radiation significantly greater than background levels. Emergency workers are not traditional radiation workers (i.e., those whose occupations involve exposure to radiation and who are part of an occupational radiation dose monitoring and protection program). Although the Occupational Safety and Health Administration Standard requires monitoring of emergency workers, there is no other regulation requiring that they be provided dosimetry. Scientific Committee:: SV Musolino, Co-Chair A Salame-Alfie, Co-Chair JL Bader, DJ Blumenthal,BR Buddemeier, HA Grogan, WE Irwin, G Klemic, GR Komp, RE McBurney, J Prudhomme, RK Schlueck, JS Wieder, W Haley, Consultant, JM Smith, Staff Consultant |
 |
Report No. 178 - Deriving Organ Doses and Their Uncertainty for Epidemiologic Studies (with a Focus on the One Million U.S. Workers and Veterans Study of Low-Dose Radiation Health Effects) (2018) Price: $180 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this Report is to provide guidance in the derivation of organ doses and their associated uncertainty for epidemiologic studies in general, but with a focus on the populations that make up the One Million U.S. Workers and Veterans Study of Low-Dose radiation Health Effects (MWS) coordinated by the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP). The study populations include atomic veterans, U.S. Department of Energy workers, nuclear power plant workers, medical radiation workers, and industrial radiographers. Organ doses from exposure to all the relevant external and internal sources for a given population are being derived. A free overview is available to non-members Scientific Committee :
|
 |
Report No. 177 - Radiation Protection in Dentistry and Oral & Maxillofacial Imaging (2019) Price: $90 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports No exposure to x rays can be considered completely free of risk, so the use of radiation by dentists and their assistants implies a responsibility to ensure appropriate protection. This Report provides radiation protection guidance for the use of x rays in dental practice, including the use of cone-beam computed tomography, digital-imaging devices, and handheld x-ray systems. The aim of this Report is to provide a practical radiation protection guide for dentists and their assistants. Information is presented in a clear and comprehensive format focusing on dental radiological practices. An overview of this report is freely available.
|
 |
Report No. 176 - Radiation Safety Aspects of Nanotechnology (2017) Price: $95 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report describes the current state-of-knowledge relating to nanotechnology that is relevant to radiation safety programs. The Report considers operational health physics practices that may need to be modified when nanotechnology is involved and those that can continue to be performed in the traditional manner. Specifically, this Report provides guidance on contamination control, engineered and administrative controls, personal protective equipment including respiratory protection, training, waste disposal, and emergency response. The Report includes specific guidance for conducting internal dosimetry programs when nanomaterials are being handled. Scientific Committee: Mark D. Hoover, Chairman, David S. Myers, Vice Chairman Leigh J. Cash Raymond A. Guilmette Wolfgang G. Kreyling Gunter Oberdorster Rachel Smith |
 |
Report No. 175 - Decision Making for Late-Phase Recovery from Major Nuclear or Radiological Incidents (2014) Price: $180 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports In 2008 the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) published Protective Action Guides (PAGs) for radiological dispersal devices (RDDs) and improvised nuclear devices (INDs). Guidance was offered to protect members of the public in the early, ntermediate and late phases of response to terrorist attacks with radiological devices. The optimization (of radiation protection)1 process was recommended for late-phase recovery in circumstances of widespread ontamination with radioactive material. The purpose of this Report is to provide guidance on optimizing decision making for late-phase recovery from a major RDD or IND incident. In light of the March 2011 Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) accident, the scope was expanded to include nuclear accidents. Scientific Committee: S.Y. Chen, Chairman D.J. Barnett B.R. Buddemeier V.T. Covello K.A. Kiel J.A. Lipoti D.M. Scroggs A. Wallo Advisors D.J. Allard J.D. Edwards H.A. Grogan A.F. Nisbet Consultants J.J. Cardarelli, II J.A. MacKinney M.A. Noska |
 |
Report No. 174 - Preconception and Prenatal Radiation Exposure: Health Effects and Protective Guidance (2013) Price: $185 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP Report No. 174, Preconception and Prenatal Radiation Exposure: Health Effects and Protective Guidance, updates and expands the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) Report No. 54, Medical Radiation Exposure of Pregnant and Potentially Pregnant Women (1977). Scientific knowledge has increased and public concerns have changed in the 36 y since NCRP Report No. 54 was published. The scope of NCRP Report No. 174 covers both ionizing radiation sources and specific nonionizing sources [i.e., magnetic-resonance imaging (MRI), ultrasound imaging, and radiofrequency (RF) fields]. This Report provides information on the types, sources and magnitudes of ionizing radiation exposures of reproductive relevance. Ionizing radiation exposures from medical care (diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, including radiopharmaceuticals) are addressed as well as from occupational sources, common environmental exposures, and from accidental or deliberate (e.g., a terrorist act) releases of radionuclides. The ionizing radiation sources discussed consist predominantly of low linear energy transfer (LET) radiation (e.g., x rays from prenatal medical procedures). The risks from ionizing radiation exposure are examined in detail from preconception through pregnancy, and during the nursing of infants. Outcomes and associated risks from preconception exposure that were evaluated include: infertility, stillbirths, birth defects, genetic alteration, and cancer. Outcomes and associated risks from exposure during pregnancy that were evaluated include: congenital malformations, growth retardation, embryonic and fetal death, mental retardation and neurobiological effects, and cancer. Also discussed is the risk to the nursing infant from the transfer of radioactive material through the mother's milk (e.g., milk from a mother who received a radiopharmaceutical) as well as from direct exposure due to radionuclides present in the mother's body. Methods for managing dose and reducing risk from various medical procedures are also addressed. For nonionizing sources (MRI, ultrasound imaging, and RF fields), the focus is on prenatal exposure, with limited coverage of childhood and adult exposure. Outcomes and associated risks during pregnancy that were evaluated, as relevant to exposure from a particular nonionizing source, include: low birth weight, delayed speech, dyslexia, nonright-handedness, and impaired intellectual performance. Scientific Committee: Robert L. Brent, Chairman Jerrold T. Bushberg Donald P. Frush Robert O. Gorson Roger W. Harms Linda A. Kroger Martha S. Linet Andrew D. Maidment John J. Mulvihill Shiao Y. Woo |
 |
Report No. 173 - Investigation of Radiological Incidents (2012) Price: $70 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this Report is to provide guidance for investigating radiological incidents that can occur wherever radioactive materials are handled, stored, used or transported, or where radiation generating equipment is operated. Radiological incidents have the potential to adversely impact; the health and safety of workers or members of the public, the environment, operations, and compliance with regulations. This Report provides guidance and practical information for individuals who have the responsibility of performing or overseeing investigations to include a scaled approach such that the extent and rigor of the investigation can be tailored to the severity and complexity of the incident. Guidance is provided on appointing individuals to an incident investigation team including recommendations for the training and qualifications of investigators and the use of consultants and specialists in conducting the investigation. The process of investigation includes a discussion of the initial response to the incident, including the procedures for controlling the incident scene to prevent loss of information, recovering any physical items that may have been removed, and how to gather information related to the incident. Various aspects for conducting the investigation are discussed including the initial team meeting, performance of onsite inspections, interviewing personnel involved in the incident, and collecting physical evidence. Performance of the cause analysis is reviewed including which type of cause analysis to perform. Ideas for the development of a corrective action plan and preparation of the investigation report, including legal considerations, are provided along with suggestions for scheduling, reviewing, tracking and trending the effectiveness of corrective actions. The Report will be useful to all safety personnel, managers who are responsible for operations that involve radiation, and those asked to perform an investigation of a radiological incident. Scientifc Committee: David S. Myers, Chairman Edgar D. Bailey Carol D. Berger Mary L. Birch John R. Frazier Eric M. Goldin Kenneth L. Miller John W. Poston, Sr. Kathryn H. Pryor Joshua Walkowicz James G. Yusko |
 |
Report No. 172 - Reference Levels and Achievable Doses in Medical and Dental Imaging: Recommendations for the United States (2012) Price: $75 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Diagnostic reference levels (DRLs) are used in medical imaging to indicate whether the patient radiation dose or amount of administered activity from a specific procedure are unusually high or low for that procedure. DRLs are the first step in the optimization process to manage patient dose commensurate with the medical purpose of the procedure. Achievable dose is an optimization goal, based on survey data, and typically defined as the median value (50th percentile) of the dose distribution of standard techniques and technologies in widespread use. The overarching goal is to obtain image quality consistent with the clinical objective, while avoiding unnecessary radiation. Too low an exposure, however, is also to be avoided if it results in an inadequate image. This Report represents an important continuation of NCRP reports on radiation safety and health protection in medicine and lays the foundation for the development and application of DRLs and achievable doses for diagnostic x-ray examinations. The concept of DRLs is extended to procedures other than diagnostic x-ray examinations (e.g., for interventional radiology) by the use of reference levels (RLs), which represent radiation dose levels that if exceeded prompt an evaluation of the reasons why. This Report discusses the establishment and use of RLs for fluoroscopically-guided interventional (FGI) procedures and describes why a different approach from DRLs is required to account for the greater complexity of interventional radiology compared with standard medical imaging procedures. Phantoms are models of the human body used in radiation dosimetry studies to estimate exposures to patients. The use of phantom survey data in the United States is contrasted with the use of patient-based dose data in Europe for establishing DRLs, achievable doses, and RLs. The use of phantom survey data is reviewed for determining DRLs for imaging modalities such as projection radiography, fluoroscopic imaging, computed tomography (CT), and for FGI procedures. Fundamental units for measuring patient dose and clinical dosimetry methods for characterizing patient dose are provided (including CT dosimetry). Data sources for establishing DRLs, achievable doses, and RLs are described. In particular the Nationwide Evaluation of X-Ray Trends (NEXT) data are discussed with regard to their applicability and limitations. A survey of the literature is provided of adult radiography and fluoroscopy, pediatric chest radiography, pediatric fluoroscopy, digital radiography, and dental radiography including intraoral, cephalometric, panoramic, and cone-beam CT. Recommendations are made on DRLs, achievable doses, and RLs for radiographic and fluoroscopic examinations, CT examinations, FGI procedures, dental radiography, and nuclear medicine procedures. This guidance can be used by medical imaging practitioners (physicians, physicists and technologists) to optimize examination techniques with reductions in radiation dose if warranted while maintaining or improving image quality. The timeliness of this Report coincides with the notable increases in radiological imaging procedures performed in the United States over the past decades. While written with the medical practitioner in mind, the Report is intended to reach a broad audience of all interested in radiation safety and health protection in medicine. Scientific Committee: James A. Brink, Chairman John M. Boone Jerrold T. Bushberg Kate A. Feinstein Jeff M. Michalski Robert J. Pizzutiello David C. Spelic Stuart C. White Judy Yee |
 |
Report No. 171 - Uncertainties in the Estimation of Radiation Risks and Probability of Disease Causation (2012) Price: $170 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Uncertainty is a measure of the lack of sureness or confidence in the results of measurements, the predictions of models or the conclusions of investigations. Uncertainty can arise from random (stochastic) variability or from the absence of relevant information or knowledge. Uncertainty analysis has become increasingly sophisticated and new methods are being developed and becoming available. The issue of uncertainty in estimation of radiation-induced risks of cancer, noncancer diseases, and heritable genetic effects analyzed in this Report is of great importance in evaluating the effects of ionizing radiation on human health, in decisions involving the safe use of ionizing radiation, in addressing public controversy and in the calculation of the probability of disease causation (assigned share) used in evaluating claims for compensation of workers who developed cancer after being exposed to radiation. This Report builds upon the analyses in NCRP Report No. 158 (2007) and NCRP Report No. 164 (2009) of sources and magnitude of uncertainties in the estimation of doses from external and internal sources of radiation. Topics addressed include uncertainties in: epidemiological methods; radiation dose estimation; selected radioepidemiological studies: atomic bomb survivors, Mayak workers, breast cancer cohorts, underground miners, populations exposed to indoor radon, and several other occupationally- and medically-exposed groups; cancer and noncancer health effects;heritable effects; risk assessments as applied to radiation protection; and excess lifetime risk projection and probability of causation of a specific disease. This Report also covers how animal and cellular data can be used in support of epidemiological studies, how dose-response relationships are generalized from one population to another, how meta-analyses and pooled analyses are applied, how dose uncertainty in epidemiological dose-response analyses are accounted for, and suggests several approaches that could reduce uncertainties in future investigations. The Report has something for everyone interested in radiation health effects, radiation protection and the application of radiation knowledge in radiation policy issues of societal importance. Scientific Committee: R. Julian Preston, Chairman John D. Boice, Jr. A. Bertrand Brill Ranajit Chakraborty Rory Conolly Richard W. Hornung Dale Preston Roy E. Shore Gayle E. Woloschak |
 |
Report No. 170 - Second Primary Cancers and Cardiovascular Disease After Radiation Therapy (2011) Price: $180 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Advances in cancer therapy, early detection of cancer, and supportive care have contributed to steady gains in the five year relative survival rate for all cancers considered together, reaching 66.1 % between 1999 to 2006. These successes are associated with a tripling of the number of cancer survivors in the United States since 1971, and the numbers are growing by 2 % each year. As of 2007, there were ~12 million men and women in the United States with a history of cancer, representing 3.5 % of the population. Radiation remains a cornerstone of successful cancer treatment, with 50 % of all patients estimated to have received radiation therapy for the management of their cancer. For many patients, the gains in survival have come at the price of serious treatment-associated late effects. Second primary cancers (SPCs) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) are two of the most frequent and important life-threatening events associated with radiation therapy. Multiple primary cancers now account for approximately one in six of all incident cancers reported each year to the National Cancer Institute Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program. NCRP Report No. 170, Second Primary Cancers and Cardiovascular Disease After Radiation Therapy, provides a comprehensive and current assessment of the risk of SPC and CVD following radiation therapy among the growing number of cancer survivors worldwide. The Report focuses on the complex epidemiologic and dosimetry issues surrounding past, conventional, and the new radiation therapy modalities and techniques, including intensity-modulated radiation therapy and proton-beam therapy. Major epidemiologic studies are reviewed that have provided estimates of the risk of SPC and CVD following exposure to therapeutic doses of radiation in children, adolescents, and adults. Special attention is given to those cancer sites for which dose-response relationships between radiation dose and SPC or CVD have been provided. There is a wealth of knowledge on the risk of SPC following radiation therapy indicating clear increases following high-dose and scatter-dose radiation. For example, radiation-specific increases in the risk of second cancers have been reported for breast, lung, thyroid, brain, bone, soft tissue, and leukemia. Quantitative estimates of risk for CVD are just now emerging and are an important area of future research. Past and current approaches to estimate individual specific doses to organs outside the primary treatment fields from various radiation modalities are summarized in this Report. The target audience for this Report is broad, including oncologists, clinicians, epidemiologists, patients, medical physicists, health physicists, dosimetrists, pediatricians, cardiologists, health-care professionals, and government personnel involved with radiation and cancer treatment issues. The Report ends with a summary of recommended research initiatives that could be undertaken to advance knowledge on the risk of developing SPC or CVD following radiation therapy in the treatment of a first primary cancer. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: Lois B. Travis, Chairman John D. Boice, Jr., Vice Chairman James M. Allan Kimberly E. Applegate Louis S. Constine Ethel S. Gilbert Ann R. Kennedy Andrea Ka-Min Ng Ching-Hon Pui James A. Purdy Xie George Xu Joachim Yahalom |
 |
Report No. 169 - Design of Effective Radiological Effluent Monitoring and Environmental Surveillance Programs (2010) Price: $105 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report is intended to support the design and operation of integrated radiological effluent monitoring and environmental surveillance. Performing monitoring and surveillance as a combined program allows each element to contribute its own strengths, with a built-in system for checking the results of one with the results of the other. Radionuclides that are important contributors to radiation dose are often at relatively high concentration at points of release, where they can be monitored with ease and accuracy so that their concentrations at points of exposure can be estimated according to a computational model. Meanwhile, the surveillance program can detect these radionuclides near points of exposure or at least show them to be below concentrations of concern. These paired measurements also can ascertain whether the release and exposure points are suitably located and instrumented, and whether the transport calculations for these releases are credible. The Report emphasizes: - designing credible programs; - presenting tried and true methods; and - integrating technical and methodological developments. Scientific Committee: Bernd Kahn, Chairman James D. Berger John A. Glissmeyer Carl V. Gogolak Norbert W. Golchert Richard E. Jaquish Janet A. Johnson Shyan K. Nair John E. Till, Advisor Richard Conatser, Consultant Bruce A. Napier, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 168 - Radiation Dose Management for Fluoroscopically-Guided Interventional Medical Procedures (2010) Price: $165 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report is focused on the use of fluoroscopic systems as a tool for guiding diagnostic and therapeutic procedures because higher radiation doses (compared to conventional radiography and fluoroscopy) are received regularly from some types of FGI procedures and occasionally from many other types of FGI procedures. Other medical applications of fluoroscopy (e.g., examination of the gastrointestinal system, guiding open surgical procedures) are outside the scope of this Report. Computed-tomography-guided interventional (CTGI) procedures are not discussed in detail due to continuing changes in the technology driven by the evolution of multi-slice computed tomography (CT) detectors. However, the principles presented in this Report are generally applicable to these domains. Most of the recommendations contained in this Report should be applied in all settings where fluoroscopic guidance is used. Within the context of radiation dose management, the goal of this Report is to supply information that helps optimize patient outcomes without compromising worker safety. However, radiation is not the only risk to which patients and workers are exposed. In many cases, radiation is a minor component of overall risk. In these situations, too great a focus on radiation safety (e.g., the use of unnecessarily thick lead aprons) may reduce the overall safety of patients or workers. Some beneficial, clinically-justified FGI procedures, even when optimized for radiation protection, deliver substantial doses of radiation to patients. This puts the patient at risk for radiogenic stochastic effects and occasionally induces radiogenic deterministic effects. However, a complete risk analysis usually identifies many other procedural hazards and will often conclude that radiation is one of the lesser hazards from FGI procedures. While the decision to conduct an FGI procedure assumes that the use of ionizing radiation is warranted by the disease state for which the patient undergoes treatment, the benefits, risks, and alternative procedures that do not require the use of ionizing radiation should be considered. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: Stephen Balter, Chairman Beth A. Schueler, Vice Chair Donald L. Miller, Vice Chair Jeffrey A. Brinker Charles E. Chambers Kenneth F. Layton M. Victoria Marx Cynthia H. McCollough Keith J. Strauss Louis K. Wagner Six Consultants |
 |
Report No. 167 - Potential Impact of Individual Genetic Susceptibility and Previous Radiation Exposure on Radiation Risk for Astronauts (2010) Price: $85 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report was prepared to evaluate the potential impact of individual genetic susceptibility and previous radiation exposures on radiation associated health risks for astronauts during their lifetimes following space missions. The Report also evaluates whether either of these factors needs to be included in the radiation protection program for astronauts. Scientific Committee: Antone L. Brooks, Co-Chairman William F. Morgan, Co-Chairman Joel S. Bedford Keith H. Dinger Roger W. Howell Ritsuko Komaki Roger P. Shaw Five Consultants |
 |
Report No. 166 - Population Monitoring and Radionuclide Decorporation Following a Radiological or Nuclear Incident (2010) Price: $95 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report is the second of two reports by the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NCRP) that focus on measurement of radionuclides deposited internally in a population exposed in a radiological or nuclear incident. The first report, NCRP Report No. 161, entitled Management of Persons Contaminated with Radionuclides (NCRP, 2008a), is an update and expansion of NCRP Report No. 65, Management of Persons Accidentally Contaminated with Radionuclides (NCRP, 1980) that provides detailed guidance for many radionuclides in a much broader range of exposure scenarios. The present Report focuses on screening a population exposed to one or more radionuclides that may be involved in a radiological or nuclear incident. Scientific Committee: Richard J. Vetter, Chairman Steven M. Becker Eugene H. Carbaugh James R. Cassata Scott Davis Fun H. Fong, Jr. P. Andrew Karam Steven H. King Adela Salame-Alfie Lin-Shen Casper Sun Katherine Uraneck George J. Vargo |
 |
Report No. 165 - Responding to a Radiological or Nuclear Terrorism Incident: A Guide for Decision Makers (2010) Price: $0 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP Report No. 165, Responding to Radiological or Nuclear Terrorism Incidents: A Guide for Decision Makers, provides the most comprehensive summary to date of recommendations and key decision points for planners preparing responses to radiological or nuclear terrorism incidents. It is unique because it considers both forms of terrorism within one publication while accounting for their fundamental differences. It is not uncommon for radiological or nuclear terrorism incident planning preparations to be broadly addressed together in a single radiation-specific hazard response publication. The potential consequences of nuclear terrorism are radically different from those of radiological terrorism and therefore the planning and preparation must take into account these differences. This Report accounts for those differences, yet draws from the characteristics that are similar for the two basic incident scenarios. This Report is intended to support preparedness efforts by providing a framework of key recommenda-tions and decision points needed by decision makers preparing for the response to a radiological or nuclear terrorism incident. This Report is consistent with, and builds upon, existing U.S. federal policy and guidance. NCRP strongly recommends that key decision makers use and understand this planning guidance in its entirety to adequately begin the planning process for response to radiological or nuclear terrorism incidents or to assess existing plans. It is incumbent upon key decision makers who use this guidance to understand the recommendations and decision points. Executive Director: DA Schauer View the latest Book Review of this Report. Keywords: radiological or nuclear terrorism, decision makers, shelter, evacuate Scientific Committee: John W. Poston, Sr. Brooke R. Buddemeier Abel J. Gonzalez Robert J. Ingram Cynthia G. Jones Kathleen Kaufman John J. Lanza Edwin M. Leidholdt, Jr. Debra McBaugh Stephen V. Musolino Tammy P. Taylor Jerrold T. Bushberg, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 164 - Uncertainties in Internal Radiation Dose Assessment (2009) Price: $135 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The objective of this Report is to review the current state-of-knowledge of uncertainties in internal dose assessments, including uncertainties in the measurements that are used to perform these assessments. In a previously published report (NCRP, 2007), the current state-of-knowledge of uncertainties in external radiation measurements and dosimetry was reviewed. The scope of this Report is limited to internal radiation exposure. It is intended to be used primarily by radiation dosimetrists, including health physicists, radiation protection professionals, and medical physicists who need to evaluate of the uncertainties in estimates of absorbed doses. The scope of application ranges from the improvement of routine dosimetry procedures to the reconstruction of individual doses in epidemiological studies to treatment planning for therapeutic nuclear medicine. Sections 1 to 4 are descriptive in nature and do not present a high level of technical difficulty and so may provide useful knowledge to health physicists, radiation protection professionals, and medical physicists who are involved in the assessment of doses from internal sources of radiation. Sections 5 to 10 are more technical and address issues of interest to health physicists involved in the assessment of uncertainties. The appendices, in which details of various methods and models are presented, are meant to be read by those scientists interested in a particular issue. Scientific Committee: Andre Bouville, Chairman A. Iulian Apostoaei Wesley E. Bolch Anthony C. James Kimberlee J. Kearfott Guthrie Miller Dunstana Melo David J. Pawel Charles A. Potter George Sgouros Richard E. Toohey |
 |
Report No. 163 - Radiation Dose Reconstruction: Principles and Practices (2009) Price: $165 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Radiation dose reconstruction is the retrospective assessment of dose to identifiable or representative individuals or populations by any means. In this Report, the scope of dose reconstruction includes estimates of absorbed dose to individual organs or tissues for specified exposure situations in support of epidemiological studies or compensation programs, to guide interventions in accidental or malevolent exposures, or for individual or public information. For the purpose of this Report, dose reconstruction excludes demonstration of compliance with regulatory criteria for workers or members of the public, and projections of dose from future or prospective exposures. There are many different applications of dose reconstruction as defined here, many potential approaches, and a great deal of scientific and public interest in the results. This Report illustrates the breadth of the field, and emphasizes that all dose-reconstruction projects, while unique, incorporate a few basic elements, which are described and illustrated with many examples (case studies). Each case study is intended to demonstrate how specific limitations associated with the case study were overcome. ISBN 978-0-9823843-1-2 Executive Director: DA Schauer Scientific Committee: Bruce A. Napier, Chairman Lynn R. Anspaugh Robert D. Daniels George D. Kerr David C. Kocher Kenneth J. Kopecky James W. Neton Steven L. Simon Richard E. Toohey Paul G. Voilleque Elena Buglova, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 162 - Self Assessment of Radiation-Safety Programs (2009) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this Report is to provide guidance for performing self assessments of radiation-safety programs. The self-assessment process is important for all institutions that use radioactive material or radiation-generating devices. These institutions range from a college using small radioactive sources in the physics department to a large nuclear power plant complex. Of course, the extent and rigor of a self-assessment program will be tailored to the size and complexity of the radiation-safety program at the institution. ISBN 978-0-9823843-0-5 Scientific Committee: DS Myers, Chairman ED Bailey CD Berger ML Birch SJ Engelhardt JR Frazier EM Goldin KA Higley JO Lubenau JW Luetzelschwab KL Miller JW Poston, Sr. KH Pryor J Walkowicz JG Yusko |
 |
Report No. 161 - I - Management of Persons Contaminated With Radionuclides: Handbook II - Management of Persons Contaminated With Radionuclides: Scientific and Technical Bases (2008) Price: $290 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP Report No. 161, Management of Persons Contaminated with Radionuclides, provides guidance to those who may be called to respond to radionuclide contamination incidents. Such incidents may range from situations in which one or a few persons have received minor contamination while working in research, medical facilities, or industry to those in which large numbers of people are contaminated as a result of accidental or deliberate releases of large quantities of radionuclides. The focus of this Report is on the medical management of individuals exposed to and potentially contaminated with radionuclides in such incidents. Thus, it is directed to persons who would provide medical care and those who would perform radiation-safety functions. This Report is an update and expansion of NCRP Report No. 65, Management of Persons Accidentally Contaminated with Radionuclides. This publication includes the both part I and II of Report No. 161 on Management of Persons Contaminated with Radionuclides, which has been published by NCRP as a two-volume series. Volume 1 of Report No. 161 is a Handbook to assist responders to radionuclide contamination incidents. Volume 1 (Section 1 through 15) contains quick reference information needed by emergency responders, recommendations for onsite and prehospital, treatment of contaminated patients at a medical facility, and post-hospital follow-up of patients and contamination control in handling decedents. Volume 2 (Sections 16 through 22 and Appendices A to J) of Report No. 161 contains extensive information on the Scientific and Technical Bases for the guidance provided in Volume 1. Included are a detailed presentation on the radiobiology of internally-deposited radionuclides, a discussion of sources of potential contamination in both planned (e.g., medical or industrial) and unplanned (e.g., nuclear accidents or acts of terrorism) settings, roles and responsibilities of responders to incidents involving radionuclide contamination, extensive dosimetry and case studies for radionuclides of 24 important chemical elements, and guidance on dose assessment methodologies. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-99-4 Executive Director: DA Schauer View the latest Book Review of this Report. Keywords: radionuclides, contamination Scientific Committee: William J Bair, Chairman Wesley E. Bolch William E. Dickerson Keith F. Eckerman Ronald E. Goans P. Andrew Karam Richard W. Leggett Joyce L. Lipsztein Michael G. Stabin Albert L. Wiley Bryce D. Breitenstein, Jr. Eugene H. Carbaugh |
 |
Report No. 160 - Ionizing Radiation Exposure of the Population of the United States (2009) Price: $140 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Detailed information on the exposure of the U.S. population to ionizing radiation, based on evaluations made in the early 1980s, was presented by NCRP in Report No. 93. Since that time, the magnitude and distribution among the various sources of radiation exposure to the U.S. population have changed primarily due to increased utilization of ionizing radiation in diagnostic and interventional medical procedures. Documented in this Report are the contributions from all radiation sources in 2006. There are clearly two major contributors to the exposure of the U.S. population from ionizing radiation: exposure to ubiquitous background radiation and medical exposure of patients. ISBN 978-0-929600-98-7 Executive Director: DA Schauer View the latest Book Review of this Report. Keywords: radiation exposure, medical imaging, radon, US population Scientific Committee: Kenneth R. Kase, Chairman Five subcommittee chairmen Thirty two committee members |
 |
Report No. 159 - Risk to the Thyroid from Ionizing Radiation (2008) Price: $160 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 159, Risk to the Thyroid from Ionizing Radiation, is an update of NCRP Report No. 80, Induction of Thyroid Cancer by Ionizing Radiation, first published in 1985 and reprinted in 1987. This Report is intended to be comprehensive and to serve as an authoritative reference on risks to the thyroid from ionizing radiation and other relevant topics. The conclusions of NCRP Report No. 159 differ significantly from those of the earlier NCRP Report No. 80. Major sources of new data have been published since 1985 that have resulted in a reevaluation of the risk models for thyroid cancer following radiation exposure. In addition, studies of the large population who were exposed when they were children and adolescents to radioiodines released as a result of the Chernobyl nuclear reactor accident have begun to provide further insight into the effectiveness of radioiodines in causing thyroid cancer. For the population at greatest risk (ages 0 to 14 y), NCRP Report No. 159 preferred model predicts a lifetime risk that is up to 1.5 times greater than that in NCRP Report No. 80. For the entire population, the risk is less in the new Report. ISBN 978-0-929600-97-0 Scientific Committee: Henry D. Royal, Chairman Seven members, two consultants and one advisor |
 |
Report No. 158 - Uncertainties in the Measurement and Dosimetry of External Radiation (2007) Price: $160 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The objective of this Report is to review the current state-of-knowledge of uncertainties in external radiation measurements and dosimetry, and in the conversion coefficients used to relate such measurements to absorbed dose in the human body. The scope of this Report is limited to external radiation exposure only. The emphasis is on uncertainty in the types of measurements used both currently and in the past for the most common occupational and environmental exposure scenarios. Although the Report does not focus directly on medical diagnostic and treatment dosimetry, some of the concepts discussed should be useful for assessing the uncertainty in measurements in this area. The focus is on the uncertainties in measurements of beta, gamma and neutron radiation from sources external to the body and the conversion of the measured quantities to organ absorbed dose. Although the current Report deals only with external radiation exposure situations where at least some measurements were available, many broader dose reconstruction uncertainty issues for which individual dosimetry is limited will require a more elaborate analysis involving one or more models. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-96-3 View the latest Book Review of this Report. Keywords: measurements, dosimetry, uncertainty, statistics Scientific Committee: Harold L. Beck, Chairman Leslie A. Braby Frederick M. Cummings Kenneth R. Kase Thomas B. Kirchner David A. Schauer Stephen M. Seltzer Steven L. Simon Christopher G. Soares R. Craig Yoder |
 |
Report No. 157 - Radiation Protection in Educational Institutions (2007) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this Report is to provide guidance for the safe use of ionizing- and nonionizing-radiation sources in educational institutions, including both teaching and research activities. Brief explanations of the terms radiation, ionizing radiation, and nonionizing radiation are given in the Glossary. To take advantage of the benefits of using radiation sources in these activities, it is necessary to provide radiation safety controls commensurate with the potential hazard. Since the sources of radiation used in many educational institutions usually produce only low radiation levels, the potential hazard to faculty, staff and students is usually correspondingly low when simple basic precautions are followed. This Report is intended primarily for those institutions that do not need a full-time radiation safety professional because the uses and radiation levels of the sources are limited. In these instances, an individual with limited expertise in radiation safety (e.g., a professor, teacher, researcher, or general safety staff member) could assume the responsibility for implementing the radiation safety program. Usually, this individual is called the radiation safety officer (RSO). This individual may have other safety responsibilities in addition to radiation safety. Full-time RSOs may also find this Report helpful. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-94-9 View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: Susan M. Langhorst, Chairman Edgar D. Bailey Mary L. Birch Susan J. Englehardt John R. Frazier Eric M. Goldin Kathryn A. Higley Joel O. Lubenau John W. Luetzelschwab Kenneth L. Miller David S. Myers John W. Poston, Sr. |
 |
Report No. 156 - Development of a Biokinetic Model for Radionuclide-Contaminated Wounds for Their Assessment, Dosimetry and Treatment (2006) Price: $140 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The scientific literature contains case reports on >2,100 wounds contaminated with radionuclides. The vast majority of these reported wounds have occurred in the proximal and distal phalanges of workers in facilities that process plutonium. Since 1990 the use of depleted uranium (DU) in military munitions has resulted in combat wounds with DU shrapnel. In addition to contaminated wounds arising in industrial and military situations, medical use of radioactive material as a radiographic contrast agent has resulted in the development of granulomas at injection sites, a type of foreign-body reaction complicated by the radiation delivered to the site. Although numerous biokinetic and dosimetric models for intakes of radionuclides by inhalation and ingestion have been published, a comparable consensus model for intake via contaminated wounds has not, even though the total amount of activity associated with a contaminated wound is typically much larger than that associated with worker exposures via inhalation or ingestion. Thus, in the mid-1990s NCRP in collaboration with the International Commission on Radiological Protection established a scientific committee tasked with developing such a wound model. NCRP Report No. 156 presents a comprehensive review and in some cases, reanalysis of animal data relating to the biokinetic behavior of radionuclides in wounds. The data have been used to derive the parameters of a comprehensive compartmental model for contaminated wounds, while the structure of the model itself is grounded in the biochemical and physiological response of the body to a wound. Information is also presented on the etiology of radionuclide-contaminated wounds, and the biological processes of wound healing, including foreign-body responses and carcinogenesis. Human data from occupational, military and medical exposures are provided to relate the animal data to human experience. Dose coefficients for local doses are presented, as is a summary of wound monitoring methodology. The development of systemic dose coefficients based on the wound model for all commonly encountered radionuclides is beyond the scope of this Report, but should be undertaken in the future. Finally, current procedures for the medical management of contaminated wounds are discussed. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-93-2 View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: Bryce D. Breitenstein, Jr., Chairman Eric G. Daxon Patricia W. Durbin Ronald E. Goans Raymond A. Guilmette John J. Russell Richard E. Toohey Fletcher F. Hahn, Advisor Jean Piechowski, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 155 - Management of Radionuclide Therapy Patients (2006) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP Report No. 155, Management of Radionuclide Therapy Patients, is intended for use by a wide readership including physicians, medical physicists, health physicists, administrators, nurses, other professional and medical staff, and patients. The approaches originally suggested in NCRP Report No. 37, Precautions in the Management of Patients Who Have Received Therapeutic Amounts of Radionuclides (1970), are incorporated and updated. This Report makes recommendations on explaining risks from therapeutic procedures and obtaining adequate, informed patient consent; dose limits for members of the patient's family; patient confinement in a hospital or skilled-care facility; and patient records including the radionuclide and activity used, the treating physician, and contact information. Section 1 of Report No. 155 is an introduction and includes some brief historical items. This Section discusses the basic principles of both radiopharmaceutical therapy and brachytherapy. Section 2 deals with basic radiation safety principles in a medical facility and includes a description of the radiation safety program, dose limits, staffing and definitions specific to this Report. Section 3 addresses radiopharmaceutical therapy including both clinical and radiation safety aspects. Appendices A and B expand on the patient release criteria outlined in Section 3 and include a spreadsheet program for assisting in determining patient release instructions. Section 4 deals specifically with brachytherapy including techniques, terminology, and a brief discussion of applicable dosimetry. Section 5 includes facility design for both nuclear-medicine and radiation-oncology installations. Section 6 describes changes in patients' status, including medical emergencies and includes guidelines for other situations that may be adapted to readers' facilities. Appendix C presents a discussion of quality-assurance requirements for high dose rate afterloading which is an increasingly useful modality. Appendix D outlines shielding requirements for high dose rate brachytherapy installations. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-92-5 Scientific Committee: Jean St. Germain, Chairman Edward B. Silberstein Richard J. Vetter Jeffrey F. Williamson Pat D. Zanzonico Jerrold T. Bushberg, Liaison Sarah S. Donaldson, Liaison |
 |
Report No. 154 - Cesium-137 in the Environment: Radioecology and Approaches to Assessment and Management (2006) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The overall goals of this Report are to summarize the current state of knowledge on radiocesium in the environment and to identify future management issues concerning Cs-137 contaminated ecosystems. Current knowledge and concepts are described concerning sources, levels in the general environment and at selected U.S. Department of Energy sites, environmental transport processes, parameters and models, and the management or mitigation of contaminated environments. This Report does not represent a comprehensive and exhaustive treatise on cesium in the environment. Rather, it is intended to provide a general review of knowledge about sources and levels, natural processes that explain the highly varied behavior of radiocesium in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, guidance for choosing transport parameters for dose and risk assessment models, and practical approaches that have been used to mitigate the impacts of significant levels of contamination. Uncertainties resulting from the use of generic parameters in environmental transport and exposure pathway models discouraged the adoption of specific parameters in this Report. Instead, the Report focuses on general environmental transport concepts and the ranges of parameter values that have been empirically measured or estimated in different situations. In many cases, the Report provides likely reasons for the wide ranges of parameter values that have been published. In practice, it is generally believed that site- and condition-specific measurements lead to the most credible assessments, so this approach is strongly recommended when possible. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-91-8 View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: F. Ward Whicker, Chairman Charles T. Garten, Jr. David M. Hamby Kathryn A. Higley Thomas G. Hinton Daniel I. Kaplan David J. Rowan R. Gene Schreckhise Margaret M. MacDonell, Consultant John E. Pinder, III, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 153 - Information Needed to Make Radiation Protection Recommendations for Space Missions Beyond Low-Earth Orbit (2006) Price: $85 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this Report is to identify and describe information needed to make radiation protection recommendations for space missions beyond low-Earth orbit (LEO). Current space radiation guidelines pertain only to missions in LEO and are not considered relevant for missions beyond LEO. Radiation protection in deep space is complicated because of the unique nature of the space radiation environment, which is unlike any radiation environment present on Earth or in LEO. The Executive Summary lists the major information that is needed. A summary of all needed information is included in Section 8. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-90-1 Scientific Committee: Lawrence W. Townsend, Chairman Gautam D. Badhwar (deceased) Leslie A. Braby Eleanor A. Blakely Francis A. Cucinotta Stanley B. Curtis R.J. Michael Fry Charles E. Land Don F. Smart |
 |
Report No. 152 - Performance Assessment of Near-Surface Facilities for Disposal of Low-Level Radioactive Waste (2005) Price: $85 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The search for solutions to the challenges posed by the need for long-term disposal and isolation of low-level radioactive waste has been long and complex. The Low-Level Radioactive Waste Policy Act, passed in 1980 and amended in 1985, specified that the disposal of most low-level waste not generated at U.S. Department of Energy sites is the responsibility of states or State Compacts. A critical factor in the process of determining acceptable disposal practices for low-level waste at any site is a demonstration of compliance with regulatory performance objectives. NCRP was asked to evaluate current approaches to performance assessment for near-surface disposal facilities for low-level radioactive waste, and Scientific Committee 87-3 was established to prepare a report on this subject. This Report provides a review of concepts underlying performance assessments of near-surface disposal facilities for low-level radioactive waste and approaches to conducting such assessments. This review includes discussions on the nature and scope of performance assessment, accepted approaches to conducting all aspects of a performance assessment, and unresolved issues in conducting performance assessments and applying the results. The Report also discusses a number of policy issues that affect conduct of performance assessment. Examples of these issues include the time period for complying with performance objectives, application of drinking water standards, and interpretation of performance objectives for compliance purposes. It is not the objective of this Report to present recommendations for resolution of policy issues, although the importance of such issues and other social, political and economic factors is recognized. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-89-5 View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: David C. Kocher, Chairman (1999 - 2006) Matthew W. Kozak, Chairman (1992 - 1999) William E. Kennedy, Jr. Vern Rogers (deceased) Roger R. Seitz Terrence Sullivan |
 |
Report No. 151 - Structural Shielding Design and Evaluation for Megavoltage X- and Gamma-Ray Radiotherapy Facilities (2005) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of radiation shielding is to limit radiation exposures to members of the public and employees to an acceptable level. This Report presents recommendations and technical information related to the design and installation of structural shielding for megavoltage x- and gamma-ray radiotherapy facilities. This information supersedes the recommendations in NCRP Report No. 49 (NCRP, 1976) pertaining to such medical radiotherapy facilities. Since the publication of NCRP Report No. 49, many facilities have been designed for accelerating voltages greater than the 10 MV maximum that was covered in that report. Hence recent designs have had to refer to NCRP Report No. 51 (NCRP, 1977) and NCRP Report No. 79 (NCRP, 1984) in order to account for the higher accelerating voltages and the concomitant production of neutrons. In addition, the use of barriers constructed with composite materials has become commonplace. This Report includes the necessary information for these higher accelerating voltages as well as a discussion of the various factors to be considered in the selection of appropriate shielding materials and in the calculation and evaluation of barrier thicknesses (Sections 1 through 6). Section 7 presents an extensive set of sample calculations, Appendices A and B provide supporting data figures and tables, respectively, and Appendix C discusses neutron monitoring for radiotherapy facilities. This Report is mainly intended for those individuals who specialize in radiation protection, but it will also be of interest to architects, hospital administrators, and related professionals concerned with the planning of new radiotherapy facilities. ISBN-13: 978-0-929600-87-1 View the latest Book Review of this Report. View the Virtual Library Presentation from the 2007 AAPM Summer School entitled Overview and Basis of Design for NCRP Report 151 by Raymond Wu, PhD, Grant/Riverside Methodist Hospital, Columbus, OH. Keywords: shielding, megavoltage, radiotherapy, medical physics, x rays, gamma rays Scientific Committee: James A. Deye, Chairman James E. Rodgers, Vice-Chairman Raymond K. Wu, Vice-Chairman Peter J. Biggs Richard C. McCall Patton H. McGinley Kenneth R. Kase, Liaison Marc Edwards, Liaison |
 |
Report No. 150 - Extrapolation of Radiation-Induced Cancer Risks from Nonhuman Experimental Systems to Humans (2005) Price: $75 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report reviews the scientific issues associated with the extrapolation of radiation-induced cancer risks from nonhuman experimental systems to humans. The basic principles of radiation effects at the molecular and cellular level are examined with emphasis on comparisons among various species including humans. These comparisons among species are then continued for cancers of similar cell types in the same organ system. Risk estimates are made from an observed level of effect as a function of organ dose. The major organ systems are individually considered. Extrapolation models are reviewed and include external and internal radiation exposures. ISBN 0-929600-86-X View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: David G. Hoel, Chairman Bruce A. Carnes Robert L. Dedrick R.J. Michael Fry Douglas Grahn William C. Griffith Peter G. Groer R. Julian Preston Consultants: Kelly H. Clifton Scott C. Miller Hildegard M. Shuller Thomas M. Seed |
 |
Report No. 149 - A Guide to Mammography and Other Breast Imaging Procedures (2004) Price: $125 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports "Mammography, in conjunction with physical examination, is the method of choice for early detection of breast cancer. Other methods should not be substituted for mammography in diagnosis or screening, but may be useful adjuncts in specific diagnostic situations." That affirmation of more than 40 years of experience with mammography for clinical detection, surveillance, and population screening is the primary conclusion of an intensive review of mammography practice by an expert committee of the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements as published in Report No. 149. The 389 page Report provides a guide to currently acceptable practices for conducting and interpreting mammographic studies, technical factors in exposures, equipment recommendations, and a thorough analysis of continuing controversies about benefits and risks from mammography screening programs. The new Report supersedes NCRP Report No. 85, published in 1986. Since the publication of the 1986 NCRP report on mammography, federal standards for all mammography facilities have been enacted and implemented. The 1992 passage of the Mammography Quality Standards Act made compulsory the voluntary standards developed in 1987 by the American College of Radiology (ACR). A combined certification and accreditation program involves the Center for Devices and Radiological Health of the Food and Drug Administration, inspections by state radiation control programs and performance reviews by the ACR program. The NCRP Scientific Committee reviewed the use of ultrasound, magnetic resonance, thermography, transillumination, computed tomography, and nuclear imaging. It observed that an extensive study of the value of digital mammography was underway by the ACR Imaging Network at the time of publication and that conclusions were not available. However, with many x-ray departments replacing screen-film procedures with digital imaging and electronic image handling and retrieval, significant changeovers are happening. The bulk of the Report contains detailed reviews and recommendations for technical factors of producing and processing mammograms. Quality assurance programs and periodic medical audits are recommended strongly. ISBN: 0929600843 Scientific Committee: Lawrence N. Rothenberg, Chairman Stephen A. Feig Arthur G. Haus R. Edward Hendrick Geoffrey R. Howe John L. McCrohan Edward A. Sickles Martin J. Yaffe Wende W. Logan-Young |
 |
Report No. 148 - Radiation Protection in Veterinary Medicine (2004) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 148 is concerned with the protection of individuals who may be exposed to radiation emitted by x-ray equipment and both sealed and unsealed radioactive sources in the practice of veterinary medicine. To the extent that the animal patient exposure is reduced, there is usually a proportional decrease in the occupational exposure to personnel. The Report provides guidance for the development of an effective radiation safety program and recommendations for the design of radiological facilities and for the use of radiographic, fluoroscopic and therapeutic equipment in veterinary medicine. Included are recommendations for the use of radiopharmaceuticals in diagnosis and therapy, and for the use of lasers and ultrasonic equipment. Although x-ray machines are widely used in veterinary medicine, the workload, and thus the potential exposure of both the practitioner and the technical assistants is, on the average, low. However, because practices such as restraining animals and holding film cassettes introduce risks of unnecessary exposure of staff, special attention is given in this Report to proper practices. Sections 1 and 2 consist of a Summary and Introduction. Radiation safety program requirements are specified in Section 3. The models used to determine shielding requirements are discussed in Section 4. Sections 5, 6 and 7 present details of the design, performance and operation of radiographic (including computed tomography) (Section 5), fluoroscopic (Section 6), and radiotherapy equipment (including brachytherapy sources) (Section 7), that relate to radiation safety and the protection of staff and visitors. Quality assurance procedures for radiographic applications (i.e., x-ray equipment used for imaging) are given in Appendix C. Section 8 covers radiation safety considerations, emergency response, and waste disposal related to the use of radiopharmaceuticals. Section 9 covers the nonionizing radiation safety and other associated safety concerns related to the use of lasers and ultrasound in veterinary medicine. ISBN 0-929600-85-1 Scientific Committee: Kenneth R. Kase, Chairman David D. Barbee Kenneth L. Miller Michael Walker Ronald P. Wilson John W. Poston, Sr. Anne Bahr, Consultant Gregory B. Daniel, Consultant Patrick Gavin, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 147 - Structural Shielding Design for Medical X-Ray Imaging Facilities (2004) Price: $110 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 147 (2004) presents recommendations and technical information related to the design and installation of structural shielding for facilities that use x rays for medical imaging. The purpose of structural shielding is to limit radiation exposure to employees and members of the public. The information supersedes the recommendations that address such facilities in NCRP Report No. 49, Structural Shielding Design and Evaluation for Medical Use of X Rays and Gamma Rays of Energies Up to 10 MeV, which was issued in September 1976. NCRP Report No. 147 includes a discussion of the various factors to be considered in the selection of appropriate shielding materials and in the calculation of barrier thicknesses. The Report presents the fundamentals of radiation shielding, discusses shielding design goals for controlled and uncontrolled areas in or near x-ray imaging facilities and defines the relationship of these goals to the NCRP effective dose limits for radiation workers and members of the public. The Report includes a detailed discussion of the recommended shielding design methodology for x-ray imaging facilities and provides an extensive collection of shielding data and sample shielding calculations for various types of x-ray imaging facilities. The Report is mainly intended for those individuals who specialize in radiation protection. However, it will also be of interest to architects, hospital administrators and related professionals concerned with the planning of new facilities that use x rays for medical imaging. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: Benjamin R. Archer, Co-Chairman Joel E. Gray, Co-Chairman Robert L. Dixon William R. Eide, Jr. Lincoln B. Hubbard Eric E. Kearsley Robert M. Quillin Raymond P. Rossi (deceased) Douglas R. Shearer Douglas J. Simpkin |
 |
Report No. 146 - Approaches to Risk Management in Remediation of Radioactively Contaminated Sites (2004) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 146 (2004) identifies and analyzes current guidance and practices used by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) under the License Termination Rule (LTR) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA, commonly known as Superfund) and the National Oil and Hazardous Substances Pollutions Contingency Plan in the remediation of radioactively contaminated sites. The Report identifies, analyzes and summarizes the significant differences and commonalities in current practices of NRC and EPA, and future implications of current practices as they relate to issues of public perception, uncertainty, measurability, and estimation of radiation dose and risk. The Report discusses the importance of involving state regulators and the public in establishing goals for the decontamination of radioactively contaminated sites. Since Superfund applies to contamination by both radioactive materials and chemicals, EPA's risk management approach uses cancer risk rather than dose, and this leads to some challenges in comparing the two agencies' approaches. NCRP believes that the seven conclusions set out in Report No. 146 capture the themes that delineate similarities and differences in regulatory approaches to remediation and decommissioning at radioactively contaminated sites used by the two agencies. The Report serves as an in-depth reference for radiation protection professionals interested in risk management practices applied to remediation of radioactively contaminated sites. Scientific Committee: Daniel J. Strom, Chairman Lynn R. Anspaugh James H. Flynn F. Owen Hoffmann David C. Kocher Paul A. Locke Paul J. Merges Bruce A. Napier Lauren Zeise, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 145 - Radiation Protection in Dentistry (2003) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 145 (2003) provides radiation protection guidance for the use of x rays in dental practice, including advice on shielding design for dental x-ray facilities. It supersedes NCRP Report No. 35, Dental X-Ray Protection, which was issued in March 1970. Dentists who conduct their radiology practices in accordance with the requirements and suggestions in this Report can obtain maximum benefit to the oral health of their patients and minimum radiation exposure to patient, operator and the public. All of the factors addressed in this Report are important and interrelated. Quality practice dictates that none be neglected. The technical factors, including office design and shielding, equipment design, clinical techniques, image receptors, darkroom procedures, and quality assurance are essential. However, the professional skill and judgment of the dentist in prescribing radiologic examinations and interpreting the results are paramount. Informed consent requires that dental patients be provided with information as to the benefits and risks of dental procedures, including dental radiography. This Report provides the dentist with data on the magnitude of effective doses from typical dental x-ray procedures. General statements are given that can be used to inform the patient about the nature of risks associated with these doses. Additional background on radiation risk assessment is included. Dentists are encouraged to use this information to educate their patients as opportunity provides. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: John W. Brand, Co-Chairman S. Julian Gibbs, Co-Chairman Marc Edwards Jerald O. Katz Alan G. Lurie Stuart C. White W. Doss McDavid, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 144 - Radiation Protection for Particle Accelerator Facilities (2003) Price: $115 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 144 (2003) is a substantial revision and expansion of NCRP Report No. 51, published in 1977 and entitled, Radiation Protection Design Guidelines for 0.1-100 MeV Particle Accelerator Facilities. NCRP Report No. 51 was one of the first comprehensive treatments of accelerator radiological-protection concerns. The Report revises and expands on the earlier report and includes new information on source intensities, shielding, dosimetry, and the environmental aspects of particle accelerator operation. It is primarily concerned with radiological safety aspects that are special to the operation of particle accelerators having energies above about 5 MeV up to the highest energies available, while not neglecting low-energy neutron generators. The purpose of this Report is to provide design guidelines for radiation protection, and to identify those aspects of radiological safety that are of major, or even unique, importance to the operation of particle accelerator installations and to suggest methods by which safe operation may be achieved. The Report is written from an engineering physics viewpoint and is intended to be useful to those engaged in the design and operation of accelerators, particularly in smaller institutions and organizations that do not have a large radiological-protection staff. Managers of institutional and industrial accelerator installations, health physicists, hospitals, radiological physicists, research scientists, government regulators, project engineers, and other similar specialists will also find the information contained in this Report useful. Since 1977, NCRP has issued two reports that discuss specific radiological-protection issues at particle accelerators: NCRP Report No. 72, Radiation Protection and Measurements for Low-Voltage Neutron Generators and NCRP Report No. 79, Neutron Contamination from Medical Electron Accelerators. NCRP Report No. 88, Radiation Alarms and Access Control Systems is also of interest for those who operate accelerators. One aim of this Report is to revise NCRP Report No. 51 in such a way that access to new material from the U.S. Department of Energy, the International Atomic Energy Agency, and the European Organisation for Nuclear Research is brought together in one volume. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: Ralph H. Thomas, Chairman W. Robert Casey J. Donald Cossairt Keran O'Brien Norman Rohrig Lester A. Slaback, Jr. Geoffrey B. Stapleton William P. Swanson Lutz E. Moritz, Consultant Vaclav Vylet, Consultant David R. Perry, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 143 - Management Techniques to Minimize Off Site Disposal of Low-Level Radioactive Waste (2003) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 143 (2003) details the Council's views on management techniques to minimize off-site disposal of low-level radioactive waste. Public concern and increased cost of the disposal of low-level radioactive waste (LLRW) have led to a need to address the minimization of these wastes particularly as they pertain to research laboratories and other small users of radioactive materials. The information in this Report will prove valuable not only to the generator of this waste but to those organizations responsible for licensing and regulation. Since risks associated with waste are related to the concentration of the hazardous material, the quantity and form of the waste, and the potential for dispersion in the environment, the generator's first priority should be the partial or total elimination of the source of the waste stream. Furthermore, waste that cannot be eliminated should be recycled in an environmentally safe manner. Next, waste that cannot be eliminated or recycled should, when feasible, be treated to reduce its hazards and to reduce the volume of the wastes. The final step is that of selecting a disposal method consistent with protection of the public health and the environment which is in compliance with federal and state laws and regulations. Scientific Committee: William P. Dornsife Russell S. Garcia Edward H. Rau Francis X. Masse John Psaras Anthony Wolbarst Walter Hipsher, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 142 - Operational Radiation Safety Program for Astronauts in Low-Earth Orbit: A Basic Framework (2002) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 142 (2002) details the Council's views on components of an operational radiation safety program for astronauts working in low-earth orbits. Astronauts are living and working for extended periods in low-Earth orbit (LEO) during Space Shuttle missions and construction, maintenance and operation of the International Space Station (ISS). The radiation environment they encounter in space is complex, with unique high-LET (linear energy transfer) and high-energy components, as distinct from the predominately low-LET and low-energy radiation environments encountered by most radiation workers on Earth. The primary purpose of an operational radiation safety program for astronauts working in LEO is to assess and control the radiation exposure of individual astronauts commensurate with mission tasks and the prevailing radiation conditions in LEO. An electronic (PDF) version of this Report is now available in Japanese. Contact DA Schauer (schauer@ncrponline.org) for more information. Scientific Committee: Richard J. Vetter, Chairman Ellen S. Baker David T. Bartlett Thomas B. Borak Susan M. Langhorst Stephen W.S. McKeever Jack Miller R. Julian Preston John W. Wilson Charles B. Meinhold, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 141 - Managing Potentially Radioactive Scrap Metal (2002) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP Report No. 141 (2002) contains the following eight recommendations: (1) Comprehensive and consistent national and international risk-based policies for managing PRSM need to be developed; (2) A set of uniform clearance standards to address national and international concerns needs to be developed; (3) The standards should include NORM and TENORM; (4) Regulatory control over orphan sources must be improved; (5) The processes of clearance and intervention/interception should be harmonized; (6) The use of licensed mills/brokerages as "clearing houses" for recycling should be encouraged; (7) New technologies and/or plant designs to reduce metal contamination should be developed; and (8) Steps should be taken to enhance public understanding of the clearance process. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: S. Y. Chen, Chairman William P. Dornsife H. Robert Meyer Anthony LaMastra Dade W. Moeller Daniel J. Strom James G. Yusko Joel O. Lubenau, Advisor Michael T. Ryan, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 140 - Exposure Criteria for Medical Diagnostic Ultrasound (2002) Price: $105 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 140 (2002) details the Council's current views on exposure criteria for medical diagnostic ultrasound. The Report is 574 pages consisting of 14 sections, four appendices, a glossary, a listing of symbols used in the Report, and 67 pages of references. The titles of the 14 sections are: (1) Executive Summary, 4 pages, (2) Introduction, 11 pages, (3) Nonthermal Mechanisms for Bioeffects in the absence of cavitation, 34 pages, (4) Noninertial Cavitation; Gas-Body Activation, 57 pages, (5) Nonlinear Bubble Responses; Inertial Cavitation, 35 pages, (6) Bioeffects of Noninertial Cavitation Involving Free and Stabilized Gas Bodies in Non-Mammalian Systems, 25 pages, (7) Bioeffects of Inertial Cavitation In Vitro, 42 pages, (8) Bioeffects of Acoustic Cavitation in Mammalian Tissues, 27 pages, (9) Models for Exposure Estimation in Human Beings, 37 pages, (10) Employed and Needed Sound Pressure Waveforms, 38 pages, (11) Temperature Elevation and Its Biological Effects, 57 pages, (12) Epidemiology of Ultrasound Exposure, 25 pages, (13) Summary and Conclusions, 25 pages, and (14) Recommendations, 5 pages. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: Wesley L. Nyborg, Chairman Paul L. Carson Edwin L. Carstensen Floyd Dunn Douglas L. Miller Morton W. Miller Horace E. Thompson Marvin C. Ziskin Robert E. Apfel, Consultant (deceased) Charles C. Church, Consultant Lawrence A. Crum, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 139 - Risk-Based Classification of Radioactive and Hazardous Chemical Wastes (2002) Price: $60 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 139 (2002) presents the Council's recommendations on a new system for classifying waste that contains hazardous substances, either radionuclides or hazardous chemicals. NCRP's recommendations incorporate three principles. First, the classification system is generally applicable to any waste that contains radionuclides, hazardous chemicals, or mixtures of the two. Second, waste that contains hazardous substances is classified based on considerations of health risks to the public that arise from waste disposal. Third, the hazardous waste classification system includes an exempt class of waste. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: Allen G. Croff, Chairman Michael J. Bell Yoram Cohen Leonard C. Keifer David C. Kocher Dennis J. Paustenbach Vern C. Rogers Andrew Wallo, III |
 |
Report No. 138 - Management of Terrorist Events Involving Radioactive Material (2001) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 138 (2001) provides information and recommendations regarding the radiological health and safety issues related to the threat of terrorist activities involving radioactive material. The Report identifies, evaluates, and makes recommendations regarding immediate and long-term radiological consequence-management issues, communication and coordination challenges, and public information challenges associated with these emergencies. This Report also provides recommendations on training guidelines, critical resources, and guidelines for internal and external exposure, as well as decontamination and cleanup. NCRP is aware of several existing recommendations and plans from many levels of government within the United States. Rather than reiterate this information (which is constantly evolving), our attention has been focused on the basic principles underlying effective planning and response to terrorist activities associated with the dispersal of radioactive materials. The Scientific Committee that prepared this Report reviewed the most likely radiological-threat scenarios taking into consideration release and dispersal mechanisms, lessons learned from actual disasters and large-scale radiological exercises, and current disaster plans at the local, state and federal levels. View the latest Book Review of this Report. Scientific Committee: John W. Poston, Sr., Chairman Cheri Abdelnour E. John Ainsworth Steven M. Becker Robert L. Brittigan Ian Scott Hamilton Eva E. Hickey David A. Kelm Fred A. Mettler, Jr. Jay M. Thompson Mark C. Wrobel |
 |
Report No. 137 - Fluence-Based and Microdosimetric Event-Based Methods for Radiation Protection in Space (2001) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 137 (2001) describes how long-term space missions of the future will subject space travelers to a unique radiation environment not experienced by Earth-bound populations. The space radiation environment is dominated by high-energy protons, helium ions, and to a lesser extent heavier ions. These particles are highly penetrating and many can traverse the shielding provided by the spacecraft and the self-shielding of the travelers' bodies. This circumstance plus the nuclear fragmentation of those particles that do interact create a radiation environment containing a relatively large component of highly ionizing radiation. Because it is known that different biological effects can occur from different particles of the same linear energy transfer (LET), it was suggested that perhaps introducing another formulation allowing explicitly for the variation of risk with particle type as well as LET might provide advantage over the conventional treatment utilizing the singled-valued quality function versus LET formulation. Report No. 137 explores two possible methodologies to circumvent this problem, the fluence-based approach and the microdosimetric approach. A description of the methodologies is presented, and advantages and disadvantages of each are identified. The result of an analysis where each of the approaches was applied to the same idealized shielding situation in space revealed that under the specified conditions, the difference in the risk calculated by each was less than a factor of two. Because of the closeness of these results and our present lack of biological data in the region of high-energy high-LET radiation, it was concluded that the reason to move to another methodology at present is not compelling. It is suggested that as new data become available and dosimetric techniques become more refined, the question should be revisited and that in the future, significant improvement might be realized. Scientific Committee: Stanley B. Curtis, Chairman Leslie A. Braby John F. Dicello Michael N. Gould Peter G. Groer Warren K. Sinclair Marco A. Zaider R.J. Michael Fry, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 136 - Evaluation of the Linear-Nonthreshold Dose-Response Model for Ionizing Radiation (2001) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 136 (2001) presents an evaluation of the existing data on the dose-response relationships and current understanding of the health effects of low doses of ionizing radiation. This reevaluation was carried out by Scientific Committee 1-6, which was charged to reassess the weight of scientific evidence for and against the linearnonthreshold dose-response model, without reference to associated policy implications. The evaluation was prompted by the need to reassess the common use, for radiation protection purposes, of the linear-nonthreshold dose-response hypothesis in the light of new experimental and epidemiological findings, including growing evidence of adaptive responses to small doses of radiation which may enhance the capacity of cells to withstand the effects of further radiation exposure, and new evidence concerning the possible nature of neoplastic initiation. The evaluation focuses on the mutagenic, clastogenic (chromosome-damaging), and carcinogenic effects of radiation, since these effects are generally postulated to be stochastic and to increase in frequency as linear-nonthreshold functions of radiation dose. For each type of effect, the relevant theoretical, experimental and epidemiological data are considered. Furthermore, in an effort to avoid overlooking pertinent data in the evaluation, input was obtained from authorities in the field and from the scientific community at large. Scientific Committee: Arthur C. Upton, Chairman S. James Adelstein David J. Brenner Kelly H. Clifton Stuart C. Finch Eric J. Hall Howard L. Liber Robert B. Painter R. Julian Preston Roy E. Shore Amy Kronenberg, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 135 - Liver Cancer Risk from Internally-Deposited Radionuclides (2001) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 135 (2001) updates the liver cancer risk of Thorotrast in humans. Thorotrast, a radiographic contrast medium containing naturally occurring radionuclides of thorium was widely used in the first half of the twentieth century. An increased incidence of liver cancer in this population of patients has been known for some time. Utilizing data on the liver cancer risk of Thorotrast and of low-LET radiations in animals, the liver cancer risk of low-LET radiation in humans is also estimated. Scientific Committee: Antone L. Brooks, Co-Chairman Glenn N. Taylor, Co-Chairman Steve Benjamin G. van Kaick Kurt Wegener Horst Wesch |
 |
Report No. 134 - Operational Radiation Safety Training (2000) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report emphasizes management's responsibility in training employees, and presents criteria for identifying training requirements for different groups of employees. The type of personnel to be trained is treated and an extensive coverage of the design and development of radiation safety programs is provided. The learning environment and training aids are discussed and guidance on the audit of training programs is given. This Report supersedes NCRP Report No. 71 on Operational Radiation Safety - Training. Scientific Committee: Kenneth R. Kase, Chairman Mary L. Birch John R. Frazier Steven M. Garry Duane C. Hall Kathryn A. Higley Susan M. Langhorst Joel O. Lubenau Kenneth L. Miller David S. Myers John W. Poston, Sr. |
 |
Report No. 133 - Radiation Protection for Procedures Performed Outside the Radiology Department (2000) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 133 (2000) is an 81 page document with five sections, two appendices, a glossary, and references. Section 1 introduces sources of occupational radiation exposure and compares occupational exposures in medicine with other sources of occupational exposure. Section 2 describes radiologic medical procedures that are often performed outside the radiology department and categorizes the procedures according to their potential for occupational exposure. Section 3 addresses conditions that affect potential occupational exposure such as time, distance, shielding, and orientation of radiation source, patient and operator. Section 4 addresses medical personnel monitoring and Section 5 briefly addresses the responsibility of management to provide safe conditions for both employees and patients. Appendix A provides information on the philosophy of radiation protection and the biological effects of medical x rays. Appendix B describes the x-ray imaging process for various imaging devices. This Report is intended for the use of clinical staff who conduct medical procedures, radiation protection staff, and those responsible for developing relevant employee education and training programs. Some examples of areas where employees may potentially be exposed are given in Table 1.3. Every medical facility operator should be responsible for incorporating the information contained in this Report into local operational and educational programs. Scientific Committee: Douglas R. Shearer, Chairman Libby F. Brateman Donald P. Harrington Mary E. Masterson-McGary Robert C. Murry, Jr. Raymond Rossi (deceased) |
 |
Report No. 132 - Radiation Protection Guidance for Activities in Low-Earth Orbit (2000) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this Report is to: (1) examine the new information about radiation environments in space, especially the radiation environment within vehicles in low-earth orbit (LEO), (2) to assess the risks to both women and men of various ages exposed to radiation in the light of the current risk estimates of excess cancer and other radiation effects, and (3) update the radiation protection recommendations given in NCRP Report No. 98 (NCRP, 1989). Other NCRP reports will deal with extrapolation of radiation risks from other biological systems to humans, biological research needs for deep space missions, evaluation of fluence and microdosimetric techniques as the basis for a radiation protection system for astronauts, and an operational radiation safety program for astronauts. Scientific Committee: R.J. Michael Fry, Chairman E. John Ainsworth Eleanor A. Blakely John D. Boice, Jr. Stanley B. Curtis Charles E. Land Donald E. Robbins Warren K. Sinclair Lawrence W. Townsend |
 |
Report No. 131 - Scientific Basis for Evaluating the Risks to Populations from Space Applications of Plutonium (2001) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 131 (2001) has considered in a broad sense the scientific bases needed to formulate models and define model parameters for an assessment of the risks to the general population and the environment from space applications of Pu-239. As such the following topical areas have been critically reviewed, with emphasis on the particular physical and chemical forms of plutonium pertinent to space applications: - the physical and chemical properties of Pu-238 oxides; - manufacturing processes for Pu-238 RTGs and characteristics of destroyed fuel forms; -environmental transport of released Pu-238 and Pu-239 in the atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere; -metabolism and biokinetics of inhaled, ingested and transcutaneously absorbed Pu-238 and Pu-239 in man and experimental animals; -dosimetry from both external and internal exposure to Pu-238 in the general population -experimental data on health effects from exposure to Pu-238; and -epidemiological evidence of health effects from exposure to Pu-239 and Pu-239, and human health risk factors. Scientific Committee: Raymond A. Guilmette, Chairman Fred Gelbard Wayne R. Hansen William Inkret Bruce A. Muggenburg John W. Poston William L. Robison Roy C. Thompson (deceased) George L. Voelz (deceased) |
 |
Report No. 130 - Biological Effects and Exposure Limits for "Hot Particles" (1999) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 130 (1999) addresses in considerable detail the consequences of hot particles on and near the skin, in the eye, ear, respiratory system, and gastrointestinal tract. Limits for exposures from hot particles are recommended. If exposures are maintained below the recommended limits, few, if any, deterministic biological effects are expected to be observed, and those effects would be transient in nature. If effects from a hot-particle exposure are observed, the result is an easily treated medical condition involving an extraordinarily small stochastic risk. Such occurrences would be indicative of the need for improvement in radiation protection practices, but should not be compared in seriousness to exceeding whole-body exposure limits. This Report supersedes NCRP Report No. 106, Limit for Exposure to "Hot Particles" on the Skin, published in 1989. Scientific Committee: Thomas F. Gesell, Chairman John W. Baum John W. Hopewell Michael W. Lantz James W. Osborne Bobby Scott Stephen M. Seltzer Roy E. Shore Basil V. Worgul |
 |
Report No. 129 - Recommended Screening Limits for Contaminated Surface Soil and Review of Factors Relevant to Site-Specific Studies (1999) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 129 (1999) is designed to assist in making decisions for cleanup of surface soil contaminated with radionuclides. The Report provides screening limits that can be applied to sites where the surface soil is known to be contaminated. The use of these calculated screening limits will allow reasonable judgments to be made regarding whether additional action is needed. The doses calculated with the dose factors in this Report are not appropriate for use in calculating estimates of health effects. The Report is 353 pages in length consisting of seven sections, four appendices, a glossary, references, and the standard NCRP back material. Scientific Committee: Harold L. Beck, Chairman David Baker Andre Bouville F. Owen Hoffman William L. Robison Joseph H. Shinn Steven L. Simon |
 |
Report No. 128 - Radionuclide Exposure of the Embryo/Fetus (1998) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 128 (1998) is designed to provide information on radiation dose to the embryo/fetus from radionculides in the mother. The Report has ten sections making up some 92 pages consisting of an introduction, sources of exposure, review of recommendations and regulations regarding exposure of the embryo/fetus, prenatal development, maternal-fetal exchange, prenatal irradiation effects, fetoplacental concentrations and radiation doses, estimation of embryo/fetus dose in radiation protection practice, research needs, and a summary and conclusions. A large part of this Report, 125 pages, provides biological information, fetal/placental information and radiation dose estimates for 83 radionuclides. The Report contains a glossary of terms, 40 pages of references, and an index for a total of 287 pages. Scientific Committee: Melvin R. Sikov, Chairman James S. Robertson Evelyn E. Watson Audrey V. Wegst Keith F. Eckerman, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 127 - Operational Radiation Safety Program (1998) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP Report No. 59, Operational Radiation Safety Program, was published in 1978. That report provided the philosophy, basic principles and requirements for a radiation safety program. In the intervening years, there have been many new developments including: new NCRP recommendations for limiting exposure to ionizing radiation (NCRP Report No. 91 in 1987 which was superseded by NCRP Report No. 116 in 1993); new techniques for the measurement and control of exposures and the disposal of radioactive waste; and new applications for ionizing radiation and radioactive materials. These developments served as the Council's rationale for preparing the current Report which supersedes NCRP Report No. 59. Report No. 127 reiterates the basic principles for establishing and maintaining an effective operational radiation safety program. Relevant aspects of such a program are discussed including: facility design criteria, organizationaVmanagement issues, training, internal and external radiation control strategies, radioactive waste disposal, environmental monitoring, radiation safety instrumentation, and emergency response planning. Scientific Committee: Kenneth R. Kase, Chairman 15 experts from academia, industry and government |
 |
Report No. 126 - Uncertainties in Fatal Cancer Risk Estimates Used in Radiation Protection (1997) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 126 (1997) addresses the uncertainty in the current risk estimates utilized for radiation protection. The bases for the current estimates start with the overall cancer mortality experience up through 1988 for the survivors of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. After reviewing past and present risk estimates, the Report then delves into the major parameters thought to contribute to the uncertainty in the current risk estimates utilized for radiation protection. First, the Report address the epidemiological uncertainty in the Japanese survivor data, looking at things such as biases due to errors in detection and biases due to city differences and other biases. Secondly, the Report addresses the dosimetrical uncertainty in their dosimetry data by reviewing random errors in dose and biases in gamma-ray measurements, uncertainty in survivor shielding, neutron dose, and neutron weight. Thirdly, the Report reviews the factors involved in uncertainty of transfer of radiation induced fatal cancer risks between populations such as the Japanese and United States populations. Fourthly, the Report addresses the factors influencing the uncertainty in projection of current fatal cancer risk estimates to lifetime risk. Fifthly, the Report considers the uncertainty in extrapolating risk obtained at high dose to that appropriate for low dose and low-dose rate exposure. Lastly, the Report addresses the combination of the above uncertainties. Scientific Committee: Warren K. Sinclair, Chairman Andre Bouville Charles E. Land |
 |
Report No. 125 - Deposition, Retention and Dosimetry of Inhaled Radioactive Substances (1997) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 125 (1997) provides a summary of the scientific information and mathematical models that describe respiratory tract deposition, clearance, retention and dosimetry for radioactive substances inhaled by people. The treatment of deposition and retention is applicable, as well, to nonradioactive substances. The result of the review provided in the Report is an integrated mathematical model of deposition and clearance that is suitable for calculating doses to the respiratory tract. The Report provides a framework for interpreting human exposures and related bioassay measurements. It can be used by scientists and others concerned with the effects of inhaled radioactive and chemically toxic substances to calculate approximate doses to the cells and tissues at risk. Mathematical models described in the Report are designed to predict the most likely mean values of deposition and clearance in various regions of the respiratory tract, and variations in these patterns to be expected for individuals who may differ in size, state of health and mode of breathing. An important characteristic of these models is that they provide information on particle deposition and clearance on an airway generation-by-generation basis. This approach allows a user to pinpoint an airway for the purposes of estimating initial particle deposition, or dose, at any time after deposition. Scientific Committee: Richard G. Cuddihy, Chairman Gerald L. Fisher George M. Kanapilly (deceased) Owen R. Moss Robert F. Phalen Richard B. Schlesinger David L. Swift Hsu-Chi Yeh |
 |
Report No. 124 - Sources and Magnitude of Occupational and Public Exposures from Nuclear Medicine Procedures (1996) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 124 begins with a discussion of the public significance of exposures resulting from nuclear medicine. The Report provides a brief overview of the procedures used in diagnosis and treatment of various conditions, and it also covers radioimmunoassay techniques. This is followed by a review of the concept of risk from radiation exposures. Included is a brief review of radiation effects with particular emphasis on effects from exposure to low levels of radiation. The subject of radiation exposure to individuals involved in preparing radiopharmaceuticals for administration to patients is followed by a review of exposures of others who may provide care to the nuclear medicine patient or who may be exposed incidentally. Finally, there is a discussion of radiation safety procedures to be observed when providing care to a patient hospitalized after receiving a therapeutic administration of radiopharmaceuticals. Scientific Committee: Kenneth L. Miller, Chairman Frank P. Castronovo, Jr. Arnold P. Jacobson Martin L. Nusynowitz Dennis D. Patton Sheila I. Kronenberger |
 |
Report No. 123 - Screening Models for Releases of Radionuclides to Atmosphere, Surface Water, and Ground - Vol. I and Vol II (1996) Price: $85 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 123, a two-volume report, seeks to meet the need for simple, authoritative, screening techniques to address release of radioactive materials to the environment. The techniques provided can be employed to demonstrate compliance with environmental standards for release of radionuclides to the atmosphere, surface water or ground. The Report provides the derivation of screening models for radionuclide releases, and covers, in addition to transport models for releases to the atmosphere and water, the matter of usage factors which relate to the consumption of contaminated drinking water and food by humans. The Report provides work sheets that allow the user to easily carry out a screening process for a proposed release via a few multiplicative calculations using a minimum of site-specific data and decisions. Scientific Committee: William L. Templeton, Co-Chairman John E. Till, Co-Chairman David A. Baker Richard B. Codell Charles W. Miller B. Gordon Blaylock F. Owen Hoffman Yook C. Ng (deceased) Yasuo Onishi Keith F. Eckerman, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 122 - Use of Personal Monitors to Estimate Effective Dose Equivalent and Effective Dose to Workers For External Exposure to Low-LET Radiation (1995) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP Report No. 122 provides practical recommendations on the use of personal monitors to estimate effective dose equivalent and effective dose for occupationally-exposed individuals. The Report is limited to external exposures to low-LET radiation. Recent additions to the radiation protection literature have made the recommendations possible. Marvin Rosenstein, Chairman Libby F. Brateman H. Gregg Claycamp John W. Poston, Sr. R. Craig Yoder Warren D. Reece, Consultant Michael J. Slobodien, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 121 - Principles and Application of Collective Dose in Radiation Protection (1995) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 121 assesses the usefulness and limitation of collective dose in radiation protection. The Report reviews the historical development of the term "collective dose." Then the scientific bases for the use of collective dose is summarized in the form of a major compilation of available human radiation epidemiology data. Limitations of the use of collective dose in radiation protection are then reviewed followed by sections on "Risk Assessment and Management" and "Conclusions and Recommendations". Ronald L. Kathren, Chairman John R. Johnson Dade W. Moeller Roy E. Shore Barbara J. McNeil Keith J. Schiager Robert Ullrich David A. Waite Eric J. Hall, Liaison |
 |
Report No. 120 - Dose Control at Nuclear Power Plants (1994) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 120 (1994) is the latest in a continuing series of NCRP reports addressing operational radiation safety topics. It is focused principally on dose control for the occupational exposures associated with the operation and maintenance of nuclear power plants. After providing a background and history of dose control, the Report presents quantitative methods that can be used as part of the decision-making process involved in satisfying dose limits and optimizing radiation exposure. The Report then provides an approach that management at nuclear plants can use to organize, direct and administer a program aimed at keeping doses as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA). Also provided are ways to assess the effectiveness of these programs, including evaluation techniques, program reviews, procedure reviews, and accountability procedures. Design considerations that have been successful in reducing doses at nuclear power plants are discussed in an important section of Report No. 120. Finally, the Report treats operational considerations necessary for implementing dose control during the operational lifetime of a plant. Appendices to the Report provide examples of information to be covered in pre-job ALARA briefings, pre-job ALARA checklists, and it provides an example program for a graded approach to ALARA. Scientific Committee: John W. Baum, Chairman William R. Kindley Thomas D. Murphy Dennis M. Quinn Alan K. Roecklein Robert Wilson Bruce J. Dionne, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 119 - A Practical Guide to the Determination of Human Exposure to Radiofrequency Fields (1993) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 119 is intended to constitute a compendium of general knowledge useful to those health and safety professionals concerned with evaluating radiofrequency hazards. It provides a comprehensive collection of information on various radiofrequency radiation sources and a straightforward "how to" guide for estimating the exposures associated with these sources. Major sections of the Report treat the following subjects: -- basic concepts, including definitions of terms and units -- procedures for evaluation of exposures -- instruments and measurement techniques -- recommended areas for further research and technical or engineering development. Appendices provide a quick reference source for use in assessing the relative significance of exposures from various radiofrequency sources, including a description of methods for performing practical measurements and computations. Explicit examples of exposure surveys for selected common sources are provided. Scientific Committee: Richard A. Tell, Chairman Howard I. Bassen Jules Cohen David L. Conover Carl H. Durney Ronald C. Petersen |
 |
Report No. 118 - Radiation Protection in the Mineral Extraction Industry (1993) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 118 is among a long series of NCRP reports focused on operational radiation safety. This Report resulted from recognition of the fact that the extraction and processing of virtually any mineral, not just those perceived as radioactive materials, might result in some level of radiation exposure warranting consideration of the need for radiation protection practices. The Report is aimed at managers and technical staff members who have become aware of the potential radiation problems and perceive the importance of evaluating facility design and operations from the point of view of potential radiation exposures. The Report describes the vital parts of an effective radiation safety program for mineral extraction facilities. Major sections of the Report include those on design of radiation protection programs; sources of potential radiation exposures; exposure management program; monitoring of occupational exposure; effluent monitoring and environmental surveillance; guidelines, standards and regulations; radiation emergency response planning; and radiation protection in specific applications. Scientific Committee: Richard L. Doty, Chairman Albert J. Hazle Charles E. Roessler Noel Savignac Edwin T. Still |
 |
Report No. 117 - Research Needs for Radiation Protection (1993) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 117 addresses research needs for establishing guidelines for radiation protection for ionizing radiation. The Report focuses on general fields of research for which increased information would be most useful. It enumerates 60 specific areas in which it is anticipated that additional research can make important contributions. These are covered in major sections of the report treating the following topics: cellular and molecular biology; dose determination?models, measurements, markers and exposure analysis; risk assessment; and prevention, intervention and perception. In a brief concluding section, the Report also addresses the issue of resource requirements for the needed research. Scientific Committee: S. James Adelstein, Chairman Bruce B. Boecker Barbara J. McNeil Antone L. Brooks Kenneth R. Kase Amy Kronenberg Roy E. Shore William L. Templeton |
 |
Report No. 116 - Limitation of Exposure to Ionizing Radiation (Supersedes NCRP Report No. 91) (1993) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 116 (1993) is the latest in the long series of reports on basic radiation protection criteria that began in 1934. It supersedes the predecessor in the series, NCRP Report No. 91, which was published in 1987. The current Report takes advantage of new information, evaluations and thinking that have developed since 1987, particularly the risk estimate formulations set out in Report No. 115. While the recommendations set out in this Report do not constitute a radical revision of the basic criteria, they do represent a refinement of the system enunciated in Report No. 91. Important changes include the utilization of revised tissue/organ weighting factors and the introduction of radiation weighting factors. Also noteworthy is the introduction of an allowable reference level of intake. Noteworthy too is the recommendation of an age-based lifetime limit for control of occupational exposures and a major simplification of limits aimed at controlling the exposure of the embryo and fetus. This Report, after outlining the goals and philosophy of radiation protection and the basis for exposure limits, goes on to review, in some detail, absorbed dose, equivalent dose, radiation weighting factors, and effective dose. Committed equivalent dose and committed effective dose are also introduced. Risk estimates for radiation exposure are presented and then the dose limits are enunciated. The Report also covers exposure in excess of the limits, limits for unusual occupational situations, guidance for emergency occupational exposure, and remedial action levels for naturally occurring radiation. Scientific Committee: Charles B. Meinhold, Chairman Seymouur Abrahamson S. James Adelstein Willaim J. Bair John D. Boice, Jr. R.J. Michael Fry Eric J. Hall Edward W. Webster Warren K. Sinclair, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 115 - Risk Estimates for Radiation Protection (1993) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 115 provides a comprehensive evaluation of the available sources of information on the risks attributable to exposure to ionizing radiation. The Report focuses primarily on utilization of well-developed risk estimate formulations to provide the basis for exposure limits. Particular attention is paid to the risk estimates produced by the United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) and the Committee on Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation (BEIR) in 1988 and 1990, respectively. The Report builds on these formulations to provide the necessary definitive judgements required to establish an adequate basis for estimates of risk at the low doses relevant to radiation protection. Report No. 115 examines the similarities and differences of the UNSCEAR and BEIR formulations; the methods of analysis, including dose-response relationships, risk-projection models, and derivations of risk at low dose and dose rate from data obtained at high doses and dose rate; and other sources of data of value to the formulation of basic radiation protection criteria. Scientific Committee: R.J. Michael Fry, Chairman Seymour Abrahamson Jacob I. Fabrikant Charles E. Land Roger O. McClellan William J. Schull Warren K. Sinclair Arthur C. Upton Edward W. Webster |
 |
Report No. 114 - Maintaining Radiation Protection Records (1992) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 114 is another in the series of reports concerned with operational radiation safety issues. The Report describes the elements that should enter into the design of a program for the maintenance of operational radiation safety records. The Report recognizes that radiation safety records can be used for a variety of purposes, including evaluation of a radiation safety program to insure its effective operation, provision of evidence of regulatory compliance, provision of data for epidemiologic studies, and provision of information for making or contesting, in legal proceedings, claims for radiation induced injury. The Report provides guidance for the establishment of a system of operational radiation safety records and makes recommendations about the content and management of such records. Major sections of the Report treat the following subjects: -- guidance for systematic generation and retention of records relating to radiation protection -- radiation protection program records -- individual records -- work place records -- environmental records -- radiation protection instrumentation. Scientific Committee: Roscoe M. Hall, Jr., Chairman (deceased) Joyce P. Davis Nancy A. Dreyer Peter S. Littlefield Bette L. Murphy Richard J. Vetter |
 |
Report No. 113 - Exposure Criteria for Medical Diagnostic Ultrasound: I. Criteria Based on Thermal Mechanisms (1992) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP Report No. 113 is the second in a series treating the use of ultrasound in medicine. The first report, NCRP Report No. 74, provided a comprehensive review of biological effects and mechanisms of action of ultrasound and an analysis of their implications for medical applications. This Report follows Report No. 74 with the first set of criteria for medical diagnostic ultrasound exposure?criteria based on thermal mechanisms. Report No. 113 develops quantitative guidelines based on computed upper limits to the temperature rise produced by ultrasound during medical procedures. From estimates of these upper limits for different acoustical conditions, together with information on the biological consequences of hyperthermia, result in criteria expressed in acoustical parameters. Major sections of the Report cover: -- Hyperthermia and life processes -- heat generation by ultrasound in mammalian tissues -- experimental studies of ultrasonically produced temperature elevation and associated biological effects -- the interrelationship of thermal and nonthermal ultrasonic process -- intensity and power needed in diagnostic ultrasound. Appendices to the Report provide background for calculations and information on approximations and assumptions employed in the Report. Scientific Committee: Wesley L. Nyborg, Chairman Paul L. Carson Edwin L. Carstensen Floyd Dunn Douglas L. Miller Morton W. Miller Horace E. Thompson Marvin C. Ziskin Marsh Edwards, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 112 - Calibration of Survey Instruments Used in Radiation Protection for the Assessment of Ionizing Radiation Fields and Radioactive Surface Contamination (1991) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 112 is one in a series of reports concerned with operational radiation protection issues. It was formulated in recognition of the fact that implementation of recommendations for the protection of workers and the public, as well as demonstration of compliance with the requirements of regulatory agencies, requires instrumentation and techniques for the measurement and evacuation of radiation fields and radioactive contamination. Proper calibration procedures are, of course, and essential requirement for effective measurement and evaluation. Report No. 112 is focused on the calibration of portable instruments used in dose equivalent assessment and the evaluation of surface contamination. The Report outlines the techniques and procedures necessary to characterize the desired responses of various survey instruments through appropriate calibration procedures. Major sections of the Report treat the following topics:
George E. Chabot, Chairman Seymour Block Dale M. Fleming Curtis L. Graham Bryce L. Rich Jacob Shapiro Kenneth R. Kase, Liaison |
 |
Report No. 111 - Developing Radiation Emergency Plans for Academic, Medical or Industrial Facilities (1991) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 111 provides guidance on developing radiation emergency plans and includes information on preparing and implementing an effective plan. An approach to classification of radiation emergencies is developed and examples are provided in appendices of the Report. Practical considerations in handling an emergency are discussed with emphasis on recovery, restoration and preventing a recurrence. Implementation and evaluation of emergency plans are also treated. Scientific Committee: George R. Holeman, Chairman David E. Drum Ronald L. Frederickson Daniel B. Howell Kenneth W. Price Gerald T. Lonergan Martha M. Malter Robert G. Wissink, Liaison |
 |
Report No. 110 - Some Aspects of Strontium Radiobiology (1991) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 110 reviews the radiobiology of radiostrontium, especially strontium-90. It also presents a review of the pertinent information on the metabolism and dosimetry of radiostrontium. Effects of radiostrontium are described briefly, especially as revealed in a series of long-term animal experiments. The possible extrapolation of these experiments to man is also considered. The Report provides estimates of risk to humans from the internal deposition of strontium-90. Major sections of the Report are those concerned with metabolism of radiostrontium, dosimetry of strontium-90 effects of strontium-90 as seen in the long-term animals studies, effects of strontium-90 compared to those of radium-226, genetic effects of strontium-90, and estimated risks to humans from internally deposited strontium-90. Appendices to the Report tabulate detailed information on activity days accumulated in various forms of bone after the intake of a specified amount of a radionuclide in blood, retention functions for strontium-90, retention in skeletons and details on experimental results of one of the important research studies employing monkeys. Scientific Committee: Ray D. Lloyd, Chairman Patricia W. Durbin Robert K. Jones Noms J. Parks Roy R. Pool Harvey A. Ragan |
 |
Report No. 109 - Effects of Ionizing Radiation on Aquatic Organisms (1991) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 109 was prepared in recognition of the fact that while the control of the discharge of radioactive effluents or wastes to the aquatic environment is based on the potential exposure of humans, rational resource management requires that the potential exposure of populations of aquatic organisms be assessed and included in any consideration of the overall acceptability of proposed or expected waste disposal practices. The Report reviews the available literature on the effects of ionizing radiation on aquatic organisms, provides guidance for a dose rate below which deleterious effects to aquatic populations are acceptably low and provides a series of simple dosimetric models that can be employed to demonstrate compliance with such a standard. The Report evaluates the validity of the conclusion that adequate protection of humans ensures appropriate protection of other living thing. The Report also includes recommendations for pertinent future research. Major sections of the Report treat effects due to acute exposure, effects due to chronic exposure, cytogenetic and genetic effects, criteria for the protection of populations of aquatic organisms, environmental dosimetry and dose to aquatic organisms and man from environment radioactivity. An appendix to the Report treats dose rate estimates to aquatic biota at selected example sites. Scientific Committee: William L. Templeton, Co-Chairman B. Gordon Blaylock, Co-Chairman David W. Engel Andrew D. Kligerman Allyn Seymour John R. Trabalka Dennis S. Woodhead |
 |
Report No. 108 - Conceptual Basis for Calculations of Absorbed-Dose Distributions (1991) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 108 is designed to present an outline of the methodology of theoretical dosimetry. The calculation of dose requires a description of radiation fields in terms of sources of particles, the physics of their interaction, and receptors. With this as input, the calculation should be able to predict the flow of energy in and out of volumes of interest and to calculate the dose. It is with this that Report No. 108 is concerned. Treated are transport formalism, sources, receptors, cross sections, transport theory, including the general theorems and properties and methods of solution, Monte Carlo methods, geometric considerations, and the calculation of dose equivalent. Appendices to the Report provide information about cross sections for transport calculations, examples of absorbed dose and dose equivalent calculations, and a compilation of geometric reduction factors for standard geometries. Scientific Committee: Harald H. Rossi, Chairman R. G. Alsmiller, Jr. Martin J. Berger Albrecht M. Kellerer William C. Roesch Lewis V. Spencer Marco A. Zaider |
 |
Report No. 107 - Implementation of the Principle of As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA) for Medical and Dental Personnel (1990) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 107 is based on the fact that modern radiation protection requires that exposures be kept at levels which are as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA), economic and social factors being taken into account. This Report addresses the implementation of ALARA for occupational exposure of persons working in medicine and dentistry. Following an introduction of concepts, units and quantities, the Report treats characteristics of occupational exposure in medicine and dentistry. The ALARA requirement is then explicated, with consideration given to cost-benefit analysis, difficulties presented by the cost-benefit model of optimization, reference levels in optimization, and guidelines for determining individual reference ranges and collective range as tools for implementing ALARA. After providing a general treatment of a practical approach to implementation of ALARA, the Report goes on to detail guidance for implementation in connection with diagnostic x-ray imaging, nuclear medicine, radiation oncology and dentistry. Scientific Committee: Marc Edwards, Chairman Stewart C. Bushong Glen V. Dalrymple James G. Kereiakes S. Julian Gibbs |
 |
Report No. 106 - Limit for Exposure to "Hot Particles" on the Skin (1989) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 106 addresses the identified potential for a limited number of workers in the nuclear industry to come in contact with microscopic particles that contain beta- emitting radionuclides, the so called "hot particles." Deposition of one of these particles on the skin raises some unique problems of potential biological effects and exposure limits. The Report treats these, assessing first the biological effects of irradiation of the skin and, subsequently, evaluation of radiobiological experiments with hot particles. An exposure limit is derived in terms of the number of beta particles emitted from a radioactive particle in contact with the skin. Scientific Committee: Thomas F. Gesell, Chairman P. Donald Forbes Charles B. Meinhold William C. Roesch H. Rodney Withers R. J. Michael Fry, Consultant Roy E. Shore, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 105 - Radiation Protection for Medical and Allied Health Personnel (Supersedes NCRP Report No. 48) (1989) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 105 superseded NCRP Report No. 48, of the same title, which was published in 1976. The current document is intended to meet the needs generated by the many changes in medical practice and procedures that have occurred since the publication of NCRP Report No. 48. The Report provides information about radiation, its effects on humans, protection against radiation, and regulatory control requirements and is aimed, primarily, at individuals who have limited expertise in radiation protection terminology and principles. The first seven sections of the Report provide, for all readers, general information on radiation and its uses in medicine. A subsequent section provides pertinent job related information for personnel involved with radiation sources, with each subsection addressing individuals in a particular job category. Included are subsections for administrators, animal care personnel, clinical/research laboratory personnel, diagnostic x- ray technologists, escort personnel, housekeeping personnel, maintenance and engineering personnel, inhouse fire crews, nuclear medicine technologists, nursing personnel, pathologists/morticians, physicians (nonradiation specialists), radiation therapy technologists, security personnel, shipping and receiving personnel, and ultrasonographers. Treated in appendices of the Report are emergency procedures, special considerations for patients containing sealed or unsealed therapy sources, definitions, and sources of nonionizing radiation in medical facilities. Scientific Committee: Kenneth L. Miller, Chairman David E. Cunningham L. Stephen Graham Carol B. Jankowski Mary E. Moore Jean M. St. Germain William R. Hendee, Scientific Committee 46 Liaison Member |
 |
Report No. 104 - The Relative Biological Effectiveness of Radiations of Different Quality (1990) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 104 constitutes an extensive evaluation of the literature on relative biological effectiveness (RBE) as a function of radiation quality for a wide spectrum of biological endpoints in a variety of species and experimental systems. The goal is the identification of patterns that would bear on the use of RBE values to establish the value of the quality factor for high-LET radiations. Emphasized are studies done at small absorbed doses or using larger absorbed doses delivered at low rates to ensure relevance to the dose and time pattern of exposure pertinent to radiation protection. The Report does not attempt to define values of quality factor but rather to provide the basis for such definition, namely the experimentally determined values of RBE. Surveyed are cytogenetic effects in plant, animal and human cells, transformation and mutation in mammalian cells in vitro, hereditary effects, including dominant lethal mutations, chromosome aberrations, reciprocal translocations induced in spermatogonia, mammalian germ cell mutagenesis, nonmammalian germ cell studies, experimental carcinogenesis, and life shortening in mice. The Report emphasizes that, for essentially all endpoints examined in eukaryotic systems, RBE values appear to increase as the dose decreases and as the dose rate decreases. The Report also points out that in a wide variety of systems, the RBE value of fast (fission) neutrons at low doses and dose rates appears to be of the order of 20 or more, similar to that for alpha particles. Scientific Committee: Victor P. Bond, Chairman Seymour Abrahamson John D. Boice, Jr. R.J. Michael Fry Douglas Grahn Peter Groer Eric J. Hall George Hutchison Gayle Littlefield Charles W. Mays (deceased) Harold Smith Robert Ullrich |
 |
Report No. 103 - Control of Radon in Houses (1989) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 103 treats the important exposure problem represented by radon and its decay products. The Report evaluates the techniques available to reduce radon and radon decay-product concentrations. Background information on the public health significance of indoor radon and on the sources and behavior of this radionuclide and its airborne decay products inside houses is provided. Attention is directed to general approaches for control, source dependent control techniques, and source independent control techniques. Guidance is also provided on the selection of appropriate control techniques. The aim is to describe and evaluate various methods that can be used to control elevated concentrations of radon and its decay products inside residences, and to provide information on the relative effectiveness and costs of specific control techniques. Scientific Committee: Dade W. Moeller, Chairman Charles T. Hess Edward F. Maher Arthur G. Scott Richard J. Guimond, Consultant John H. Harley, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 102 - Medical X-Ray, Electron Beam and Gamma-Ray Protection for Energies Up to 50 MeV (Equipment Design, Performance and Use (Supersedes NCRP Report No. 33) (1989) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 102 (1989) treats equipment design and use aspects of medical imaging and therapy systems. It supersedes NCRP Report No. 33, Medical X-Ray and Gamma-Ray Protection for Energies Up to 10 MeV, Equipment Design and Use, which was published in 1968 and served the medical radiation community as a basis for the design and use of medical radiation equipment. This current report differs from the previous one in that it treats a broader energy range and addresses electron beams as well as x and gamma rays. The Report provides recommendations regarding design, performance and optimal use of equipment and also treats such matters as radiation protection surveys and personnel monitoring. Major changes in procedures and equipment have taken place since the publication of the predecessor report and in the current Report these new procedures and equipment designs are treated. Thus, for example, mammography, cardiac catheterization, and computed topographic equipment are covered. Emphasized in connection with diagnostic equipment are imaging characteristics and patient dose. In connection with radiation therapy systems, such topics as simulators are addressed, as well as the necessary equipment and facility design aspects and performance standards. In most cases, recommendations for the user are also provided. Important sections of the Report treat therapy equipment, calibration guides, radiation protection surveys, and working conditions. Scientific Committee: Earle C. Gregg, Chairman 1977-1983 (deceased) Jack S. Krohmer, Chairman 1983-1989 Robert D. Adams Harold L. Kundel Seymour H. Levitt Robert J. Nelsen William S. Properzio Gopala U.V. Rao Leonard Stanton Robert G. Waggener |
 |
Report No. 101 - Exposure of the U.S. Population from Occupational Radiation (1989) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 101 is another in the series of reports assessing exposures resulting from various sources of radiation. The Report compiles the information on exposures in a wide variety of occupational settings including nuclear power production, medical uses of radiation, industrial applications, and research activities. Review of the available data made evident the need to treat the reasons for, and the uncertainties associated with, personnel dosimetry and these are covered in the Report. Summary information is provided on the effective dose equivalents and the collective effective dose equivalents for the United States work force exposed to radiation. The results demonstrate that occupational exposures are responsible for only a small fraction of the total collective effective dose equivalent for the entire United States population. Scientific Committee: Donald E. Barber, Chairman Barbara G. Brooks Lawrence H. Lanzl Roy E. Shore Paul S. Stansbury Robert A. Wynveen |
 |
Report No. 100 - Exposure of the U.S. Population from Diagnostic Medical Radiation (1989) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 100 is one of a series of five reports providing detailed information on population exposures arising from various sources. The Report addresses the radiation dose to the population from diagnostic medical and dental x-ray examinations and nuclear medicine procedures. Detailed are data sources, the number of examinations, population demographics, differential trends, absorbed doses, gonadal and genetically significant doses, and effective dose equivalents, as well as such items as film usage, and future trends for diagnostic radiology. Considerable attention is devoted to the age distribution of populations undergoing different medical diagnostic examinations because of the import this carries for risk estimation. The Report concludes that the contribution to the annual effective dose equivalent of the United States population in terms of the average annual effective dose equivalent is 0.40 mSv for diagnostic x rays, while that for nuclear medicine is 0.14 mSv. Thus, the medical uses treated provide approximately 15 percent of the total average effective dose equivalent in the United States population. Scientific Committee: Chairmen: W.W. Burr (1972-1976) Robert D. Moseley, Jr. (1976-1987) - deceased Fred A. Mettler, Jr. (1987-1989) 12 experts from academia, industry and government |
 |
Report No. 099 - Quality Assurance for Diagnostic Imaging (1988) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 99 addresses factors that influence production of an image which contains the necessary information to enable the imaging physician to report the diagnostic findings to the referring physician. All of the management practices instituted to assure highest quality medical care constitute quality assurance and thus are the subject of the Report. However, major emphasis is given to quality control which is an essential element of quality assurance. In connection with quality control, the Report treats such matters as the establishment of a quality control program, procedures, objectives and policies, photographic quality control, quality control in conventional radiography, fluoroscopic and cine imaging and mobile radiographic capacitor discharge and fluoroscopic systems. Also treated are x-ray tomography, mammography, dental radiography, and radiological special procedures. Computed tomography, digital imaging, nuclear medicine, ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging are also addressed. Information is provided on quality control elements of video systems and computers. An appendix provides a summary of quality control tests. Scientific Committee: Andrew K Poznanski, Chairman Harry W. Fischer Joel E. Gray William R Hendee James G. Kereiakes Harold L Kundel William J. Tuddenham James A. Zagzebski |
 |
Report No. 098 - Guidance on Radiation Received in Space Activities (1988) Price: $36 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 98 develops guidance on radiation exposures occurring in space activities utilizing the vast body of information on the space radiation environment and the biological effects of radiation that has developed since 1970, when the last guidelines for space exposures were promulgated. Radiation risk estimates for carcinogenesis, genetic effects and nonstochastic effects were utilized to develop risk comparisons on which career exposure limits are based. An important result of this approach is a differentiation in limits based on age and sex. Major sections of the Report treat radiation environments in space, radiation exposure to personnel, radiobiological features of the space radiation environment, and radiation protection standards in space. The Report also identifies needed research relevant to radiation exposures in space activities. Scientific Committee: R.J. Michael Fry, Chairman John D. Boice, Jr. Victor P. Bond Stanley B. Curtis Douglas Grahn Paul W. Todd |
 |
Report No. 097 - Measurement of Radon and Radon Daughters in Air (1988) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 97 describes measurement techniques appropriate for the assessment of radon and radon daughters in both occupational and environmental situations. Information on the properties of radon is presented, with emphasis on those properties that are important in developing proper methods of measurement. Strategies for measurement in most typical situations are detailed and the methods appropriate to particular situations are described. Calibration, standardization and quality control are emphasized. Major sections of the Report treat physical properties of radon and its decay products, distribution of uranium, thorium, radium and radon in the environment, radon emanation and transport, measurement of individual decay products, measurement of potential alpha energy concentration, radon flux measurements, and calibration, standardization and quality assurance. The critical level and lower limit of detection are treated in an appendix as are units and conversion factors, and a glossary. Scientific Committee: Naomi H. Harley, Chairman Isabel M. Fisenne John H. Harley Richard G. McGregor Anthony V. Nero Marvin H. Wilkening |
 |
Report No. 096 - Comparative Carcinogenicity of Ionizing Radiation and Chemicals (1989) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 96 was prepared to evaluate the extent to which the principles and methods that have been developed for use in assessing the carcinogenic risks of ionizing radiation are applicable in assessing the carcinogenic risks of chemicals. In addressing this question, the Report reviews the status of knowledge concerning the carcinogenic effects of radiation and chemicals, with particular reference to their comparative mechanisms of actions and the dose effect relationships involved. Mathematical models for predicting carcinogenic risks from radiation and chemicals are reviewed for those exposure conditions where human data are fragmentary or lacking. Major sections of the Report treat the nature and mechanisms of carcinogenic effects, nature, distribution and sources of ionizing radiation in the environment; nature, distribution and sources of carcinogenic chemicals in the environment; carcinogenic effects of radiation and chemicals in humans; extrapolation from laboratory models to the human; and risk assessment. Scientific Committee: Arthur C. Upton, Chairman R.E. Albert J.C. Barrett G.W. Beebe D.W. Nebert A.V. Ray R.R. Tice S.H. Yuspa |
 |
Report No. 095 - Radiation Exposure of the U.S. Population from Consumer Products and Miscellaneous Sources (Supersedes NCRP Report No. 56) (1987) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 95 is another of the assessment series of reports. This Report recognizes that there are many consumer products available which emit ionizing radiation, in some cases as an essential element of the proper performance of the device and in other cases as incidental or extraneous to the purpose for which the product was designed. The Report evaluates the exposures from all of these types of products. Treated are electronic products such as television receivers and airport luggage inspection systems; radioactive materials such as radioluminous products, building materials, glass and ceramics; and miscellaneous exposure sources such as high voltage vacuum electronic units. Also covered are exposures resulting from disposal of radioactive surplus items and transport of radioactive materials. Recommendations for dose reduction are also provided in the Report. Scientific Committee: Dade W. Moeller, Chairman Richard J. Guimond John W. N. Hickey Edwin A. Miller Gail D. Schmidt |
 |
Report No. 094 - Exposure of the Population in the United States and Canada from Natural Background Radiation (Supersedes NCRP Report No. 45) (1987) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 94 is another of the reports providing detailed assessment of population exposures. Natural radiation and radioactivity in the environment provide the major source of human radiation exposure and thus a comprehensive evaluation of exposures from this source is an important aspect of the overall assessment of population exposure. This Report gives a broad picture of exposure to natural background radiation. It includes considerable descriptive material in the introductory sections and then presents data summarizing the available information on the levels of natural radiation in the environment, the consequent average exposures, and radiation doses to the population and, wherever possible, the distribution, or at least the variability, of these factors. Treated in the Report are cosmic radiation, cosmogonic radioactivity, radionuclides in the earth, external terrestrial radiation, inhaled radionuclides, internally deposited radionuclides, and unusual exposures. An appendix provides information on fallout from nuclear weapons tests. Scientific Committee: John H. Harley Richard B. Holtzman Wayne M. Lowder Dorothy P. Meyerhof Allan B. Tanner Ned A. Wogman Bernard S. Pasternack, Consultant Joseph K. Soldat, Consultant James A. Young, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 093 - Ionizing Radiation Exposure of the Population of United States (1987) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 93 (1987) provides an assessment of the average exposure of members of the United States population from all sources of ionizing radiation. This is a comprehensive statement on the total exposure of members of the United States population from all sources on the basis of a common unit, the effective dose equivalent. Considered are six main source categories: natural radiation, occupational (radiation workers), nuclear fuel cycle, consumer products, miscellaneous environmental sources, and medical diagnosis and therapy. For each of these sources, the product of the estimated number of people exposed and the average effective dose equivalent received from that source is expressed as the collective dose from that source. The collective dose from each source is then divided by the entire United States population to obtain the contribution from that source to the average effective dose equivalent for a member of the United States population. Scientific Committee: W.K. Sinclair, Chairman S.J. Adelstein M.W. Carter J.H. Harley D.W. Moeller |
 |
Report No. 092 - Public Radiation Exposure from Nuclear Power Generation in the United States (1987) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 92 is the first of a series of reports providing detailed information on population exposures as summarized in NCRP Report No. 93. The Report presents estimates of exposures arising from the entire light water reactor nuclear fuel cycle. Dose estimates are calculated for individuals in the general population who may receive the maximum exposure and for the population within 80 km of facilities that are typical of those in operation in the nuclear fuel cycle. Each process in the cycle is presented in sufficient detail to provide an understanding of the sources and magnitudes of radiations and radionculides involved. Annual release rates of radionuclides to air and water and the resulting radiation doses are given for exposures arising from mining, milling and refining, uranium hexafloride production, enrichment, fuel fabrication, power generation, fuel reprocessing, low-level waste, spent fuel storage, high-level waste, and transportation. Scientific Committee: Bernd Kahn, Chairman Michael J. Bell Richard L. Blanchard Edward F. Branagan, Jr. Kenneth Cowser Keith F. Eckerman James M. Hardin Robert E. Luna Edward Y. S. Shum Jerome F. Wing Charles Willis |
 |
Report No. 090 - Neptunium Radiation Protection Guidelines (1988) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 90 is an addition to the series of reports that treat radiation protection concerns in connection with individual radionuclides. It reviews knowledge of neptunium in areas that are important to radiation protection. Treated in the Report are chemical and physical properties of neptunium, the sources of neptunium in the environment, and potential pathways to man. Since the gastrointestinal absorption of neptunium by humans has become an important question, considerable attention is directed to the understanding that might be gained from careful review of the animal studies on metabolic behavior neptunium. Health effects are treated and radiation protection guidelines are provided. Scientific Committee: Roy C. Thompson. Chairman Maryka H. Bhattacbaryya Norman Cohen Robert P. Larsen Maurice F. Sullivan Patricia W. Durbin, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 089 - Genetic Effects From Internally Deposited Radionuclides (1987) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports It was learned in the late 1920s that ionizing radiation could produce genetic effects such as gene mutations and chromosome aberrations. However, at least until 1945, the focus of interest in radiation protection was primarily on somatic effects manifested in the individual exposed. Studies of the genetic effects of radiation using drosophila, however, refocused attention on effects transmitted to the exposed individuals offspring and concern over fallout in the 1950's resulted in efforts to estimate the genetic effects from exposure of human populations to internally deposited radionuclides. No human populations have been identified with burdens of internally deposited radioactive materials which have been shown to produce evidence of transmissible genetic damage. As a result, the research approach has been one in which macromolecular, cellular, and whole animal genetic studies have been combined to estimate genetic effects on humans following the deposition of radioactive materials in the body. The purpose of this report is to update the information available from animal and cellular experiments that relates genetic effects to deposited activity and dose from internally deposited radioactive materials. For the various radiation types, genetic data for internally deposited radioactive materials are compared with those derived from exposure to external acute or protracted radiation to estimate the relative genetic hazard. Scientific Committee: Antone L. Brooks, Choirman Douglas Grahn William L. Russell Paul B. Selby |
 |
Report No. 088 - Radiation Alarms and Access Controls Systems (1986) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports In facilities where radioactive materials are handled, or where radiation-producing equipment is used, the building, the equipment, and the associated safety procedures should be designed and developed together to provide a safe work environment. The specific combination of requirements for a given facility is defined by the operational radiation safety program. The specific elements to consider when establishing a new facility are outlined in NCRP Report No. 59, "Operational Radiation Safety Program" (NCRP, 1978a). Two of the elements of an operational radiation safety program are radiation alarm and access control systems. (In NCRP Report No. 59, Section 4, these are referred to as warning and security systems.) The purpose of this report is to provide a more detailed discussion of radiation alarm and access control systems than could be provided in NCRP Report No. 59. It should be emphasized that this report describes a range of alarm and access control systems that can and do provide an acceptable level of safety at many types of facilities. Depending on circumstances, the solutions offered here may not be appropriate for certain facilities because they are too restrictive, not restrictive enough, or do not cover all circumstances. Thus, this document is offered as a starting point providing ideas that professional health physicists can adapt to meet the needs of a particular situation. Under no circumstances should this report be interpreted in "cookbook" fashion, with literal adherence to every recommendation demanded, nor should it be expected to provide adequate protection in every case without consideration of local conditions. It is also worth noting that the weakest link in any system of personnel protection is not the hardware but the people themselves. The single leading cause of accidents is the failure of personnel to follow established procedures. Thus, the simplification of procedures, regular training, and replacement of administrative control with hardware that does not unduly impede the normal operation of the facility will go a long way toward reducing the potential for accidents. Scientific Committee: David S. Myers, Chairman Duane C. Hall Ronald L. Kathren Lawrence H. Lanzl Gary T. Warren Martin L. Rozenfeld, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 087 - Use of Bioassay Procedures for Assessment of Internal Radionuclide Deposition (1986) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 87 is concerned chiefly with the conceptual framework and methodology required for proper assessment of the occurrences, magnitudes and retention of internal depositions of radionuclides in humans. General information on bioassay procedures is given, as is guidance on critical elements of a bioassay program such as when bioassay is needed, who should participate, how frequently sampling should occur, how the results might be interpreted, and the limitations of bioassay data for health protection purposes. Many of the problems involved in bioassay efforts, such as errors in the measurements made, uncertainties in the models used to interpret the results, and variability among subjects in radionuclide metabolism and dosimetry are treated in the Report. Scientific Committee: Harry F. Schulte, Chairman Robert E. Alexander Bruce B. Boecker Orval L. Olson Ralph G. Smith Lloyd Tepper William D. Moss, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 086 - Biological Effects and Exposure Criteria for Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields (1986) Price: $80 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 86 presents the results of a comprehensive evaluation of the available literature on the biological effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. This Report begins with a discussion of studies of biological effects at the molecular level and continues to progressively larger scales of interaction, covering macromolecular and cellular effects, chromosomal and mutagenic effects and carcinogenic effects. The Report then goes on to treat systemic effects such as those relating to reproduction, growth and development, hematopoesis and immunology, endocrinology and the autonomic nerve function, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular effects, interaction of electromagnetic fields with the central nervous system and the special senses. The Report treats neurological effects and assesses studies relating to behavioral effects. The careful evaluation of the research studies forms the basis for the exposure criteria enunciated in the Report. These specify permissible levels, not only for individuals exposed occupationally, but for members of the general public exposed to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation. Scientific Committee: Arthur W. Guy, Chairman W. Ross Adey Edward L. Alpen (deceased) Don R. Justesen Mary Ellen O'Connor Richard D. Phillips Ten expert advisors and consultants. |
 |
Report No. 084 - General Concepts For The Dosimetry Of Internally Deposited Radionuclides (1985) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report is a necessary, formal update of the positions held and recommendations made in the 1959 NCRP report on internal emitters (NCRP, 1959), including a review of the evolution of internal emitter protection practices in the US over the past two decades. The new ICRP methods of calculating radiation doses from internally deposited radionuclides are accepted as a conceptual basis for future standards, but with significant reservations as to specific application. The models employed by ICRP for dosimetry, deposition, transport, and anatomical parameters are adopted as generally superior to those recommended by NCRP in 1959. However, some deficiencies in these models are identified. This Report is organized into four further sections. Section 3 deals with primary concepts, reviewing their evolution and stating the position of NCRP on these concepts, particularly as it may coincide with, or differ from, that of the ICRP. Section 4 considers the output of the system - the forms of expression of internal emitter standards, and the manner in which these standards are properly used. Section 5 considers in some detail the deposition, metabolism, and anatomical models which form the basis for an internal dose calculation system. The evolution of current ICRP models is traced, and areas of needed improvement and limitations on NCRP acceptance of these models are identified. Section 6 identifies research needs and Section 7 presents a concise qualitative statement of present NCRP thought on control of internal exposure. Appendices include a consideration of the effect of dosage regimes on the radionuclide content of tissue, information on the central concepts of the new ICRP dose limitation system as they relate to control of internal emitters, the new ICRP methods for calculating doses to tissues from internally deposited radionuclides, and a list of the NCRP task groups contributing to this Report. It is also pertinent to emphasize what this Report does not contain. It does not contain a detailed quantitative NCRP system for control of internal exposure; this is being developed as part of a general system encompassing both internal and external irradiation, and will be the subject of a separate report. It also does not contain numerical limits for control of exposure to radionuclides or specific recommendations for evaluation of individual exposures. Scientific Committee: J. Newell Stannard, Chairman John A. Auxier William J. Bair Patricia W. Durbin Keith J. Eckerman Roger O. McClellan Paul E. Morrow Robert A. Schlenker Roy C. Thompson Ian T. Higgins, Consultant Chester R. Richmond, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 083 - The Experimental Basis for Absorbed-Dose Calculations in Medical Uses of Radionuclides (1985) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The primary purpose of this Report is to review the current status of the methods used to estimate the radiation absorbed doses to humans from internally deposited radionuclides. Particular emphasis will be placed on comparing the results of direct measurements with calculations based on mathematical models to estimate the parameters that enter into dose calculations. Methods will be suggested which may be used to obtain good data. The Report briefly reviews the history of internal radiation dosimetry, followed by a discussion of the physical parameters and transport calculations in dosimetry. Included is a discussion of the techniques used to measure the activity distributions in humans, and the factors which should be considered in making in-viuo absorbed dose measurements. Also, comparisons of measured and calculated absorbed dose values in phantoms, animals, and humans are made. The Report includes a formalism in Appendix A that can be used to quantify the radioactivity in irregular geometric shapes using an external measurement technique. Other appendices include a glossary and symbols. Recommendations for further studies are given. Scientific Committee: James S. Robertson, Chairman Martin J. Berger Jerry P. Jones Katherine A. Lathrop John W. Poston Kenneth N. Vanek Robert G. Zamenhof |
 |
Report No. 082 - SI Units in Radiation Protection and Measurements (1985) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 82 considers the concepts of quantities and units and gives a brief history of the international system (SI). The structure of the system is discussed, including base units, supplementary units, derived units, and some special categories of units. The meaning of coherence, which is an advantage of the SI, is explained, as well as the use of prefixes in the SI. Relationships between conventional units and SI units for some quantities used in radiation measurements are discussed and examples are given of calculations in both customary and SI units. The Report also contains the Council's recommendation calling for the gradual adoption of SI units over a five-year transition period. Scientific Committee: Randall S. Caswell, Chairman Edward R. Epp William A. McCarthy Fred A. Mettler, Jr. Ralph H. Thomas Henry N. Wagner. Jr. Harold O. Wyckoff |
 |
Report No. 081 - Carbon-14 in the Environment (1985) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report summarizes the available information on C-14 in terms of its physical properties, sources, distribution in the environment, sampling and analysis, biology, projected impact, dosimetry, and waste management; and considers and evaluates its importance as a potential source of local and worldwide radiation exposure. Carbon-14 is produced naturally by cosmic ray interactions in the atmosphere. This natural source has been augmented by anthropogenic sources which include fallout from nuclear weapons testing and, to a lesser extent, emissions from nuclear power reactors. The specific activity of the atmospheric C-14 is continually reduced by the combustion products of fossil fuels and other sources which release stable carbon to the atmosphere diluting C-14 concentrations. Scientific Committee: A. Allen Moghissi, Chairman Philip W. Krey Lester Machta John M. Matuszek John R. Totter Robert W. van Wyck |
 |
Report No. 080 - Induction of Thyroid Cancer by Ionizing Radiation (1985) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this Report is to evaluate the potential of exposure to x and gamma external radiation and/or to internally deposited radionuclides to induce thyroid cancer in humans. Any such effort is necessarily subject to the constraint of limited data, and this is particularly true for radionuclides deposited in the thyroid. What human data exist relate primarily to exposure to external x irradiation or, to a much lesser degree, to internally deposited I-131. In spite of such limitations, practical protection procedures require a quantitative assessment of the potential of radiation exposure to induce human thyroid cancer. That potential is most often expressed in terms of the risk of developing radiation induced thyroid cancer. To develop risk estimates, it is necessary to examine the reports and assumptions from existing human and non-human studies. However, the transfer of inferences from animal studies to humans is perilous. In addition, large gaps in the existing data, the low incidence of thyroid cancer, and the small size of populations available for study make risk derivations uncertain. At best, the potential of radiation exposures to cause human thyroid cancer can only be approximated. This Report makes use of such data as are available to develop average risk estimates for combined populations over various ranges of radiation dose to the thyroid. The estimates are not intended and should not be used for application to individuals. Their use in any circumstances requires understanding and careful consideration of their limitations and must include evaluation of a large number of often ill-defined factors such as type and amount of exposure, time since exposure, and differences of sex, age and heredity. Since most available data on the induction of cancer by radiation are obtained from populations that received relatively large exposures, extrapolation to lower dose levels is often necessary. However, large exposures often cause cell death which can influence the incidence of observed carcinogenesis. For this reason, the dose ranges used for the calculation of risk are confined to situations in which human thyroidal carcinogenesis has been demonstrated and for which cell killing is not thought to be a serious limiting factor. Scientific Committee: H. R. Maxon. Chairman D.V. Becker S.A. Book C.R. Buncher S.R. Thomas E.L. Saenger, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 079 - Neutron Contamination from Medical Electron Accelerators (1984) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This report addresses a problem encountered with the use of electron accelerators in radiation therapy. The potential exists for the production of neutrons, in several different ways, when equipment used to generate electrons operates at energies above 10 MeV. The sources of these neutrons and their relative contributions are described. A further section is devoted to the potential hazard from the neutrons which are produced and which represent a contribution to the total radiation dose to the patient. This contribution is not normally included in the calculation of dose delivered to the treatment volume, as performed by the therapist and the medical physicist. The question of whether or not this additional dose constitutes an unacceptable risk to the patient is discussed. The Report addresses the hazard to operating personnel from neutrons produced outside the patient's treatment volume. Neutron measurement methods are also addressed. The Report concludes with a survey of the published literature relevant to the subject. Scientific Committee: Richard C. McCall, Chairman Peter R. Almond John A. Devanney Everett G. Fuller George R. Holeman Lawrence H. Lanzl Harry Ing, Advisor William P. Swanson, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 078 - Evaluation of Occupational and Environmental Exposures to Radon and Radon Daughters in the United States (1984) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 78 considers the radon daughter lung dose for both occupational and general population exposures. The Report addresses the complexity of the lung dose calculation and discusses the various factors which influence the dosimetry. The Report examines the variability of the radon daughter dose conversion factor for the underground miner, as well as for the adult male and female, child and infant in the general population. The Report describes a model for estimating lung cancer incidence from exposure to radon and its daughters at exposure levels of concern to the general population and to the miner. The Report presents calculations of the potential risk associated with the occupational radon daughter exposures and it estimates the risk to the members of the general population from exposure to an assumed average environmental level of radon daughters. Scientific Committee: Naomi H. Harley, Chairman Fred T. Cross Bruce D. Stuart Victor E. Archer, Advisor Donald A. Morken, Advisor John H. Harley, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 077 - Exposures from the Uranium Series with Emphasis on Radon and Its Daughters (1984) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 77 considers and evaluates potential exposures from the radionuclides of the uranium series with emphasis on radon and its daughters. The Report examines, on the basis of available information, the sources of radon, the levels of exposure and their probable distribution, and estimates the risks attributable to these exposures. The Report concludes that while information on levels and number of individuals exposed in the United States population is incomplete and needs to be improved, potentially the most significant radiation exposure of the United States population is that from naturally occurring radon and its daughters. The Report develops the rationale for recommendations for remedial action, specifies a level of exposure at which remedial measures need to be considered, and suggests possible remedial measures. Scientific Committee: John H. Harley, Chairman Naomi H. Harley John W. Healy George V. LeRoy Ernest G. Letourneau |
 |
Report No. 076 - Radiological Assessment: Predicting the Transport, Bioaccumulation, and Uptake by Man of Radionuclides Released to the Environment (1984) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this Report is to review the current status of the application of radionuclide transport models from the point of discharge to the environment to the point of intake by man. This process, called radiological assessment, begins by defining the quantity of radionuclides that are released and enter the environment. Uncertainties in the measurements or estimates of the source term are passed on to the assessment calculations. This Report does not specifically address the development of source terms, however it should be borne in mind that important information about source terms must be available in order to determine which radionuclide transport models to use in an assessment. This information should incorporate the proximity of different points of release, the time distribution of release, the quantity and species of radionuclides released, and the chemical and physical form of the radionuclides. In the description of the models that follow, sufficient information is presented to allow the user to determine which of the source term conditions listed above should be considered. Scientific Committee: William L. Templeton, Chairman (Task Group 2) John E. Till, Chairman, (Task Group 3) Sixteen expert members and consultants. |
 |
Report No. 075 - Iodine-129: Evaluation of Releases from Nuclear Power Generation (1983) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Considerable attention has been given to I-129 because of the potential for long-term accumulation in the environment from prolonged low-level releases from the nuclear industry, principally from facilities concerned with the separation and processing of irradiated fuels and storage of wastes. Currently, the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels is very limited, but is likely to increase in the future. If retrievable storage is the means chosen for handling spent fuel elements, I-129 will remain potentially available for release to the environment whenever reprocessing occurs, because of its slow rate of physical decay. If, on the other hand, spent nuclear fuels remain unprocessed in a permanent disposal site, then releases of I-129 to the environment from U.S. facilities described herein will be insignificant compared to the estimates given in this Report. The extent to which I-129 could be released to the accessible environment from a permanent disposal site will be determined by the design of the repository, and by conditions in the environs. The details of potential long term releases of I-129 from such repositories is beyond the scope of this Report. However, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, in proposing standards for the disposal of spent fuel, high level and transuranic radioactive wastes, indicated that the total I-129 in their model repository would be a fraction of their calculated allowable release limit (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 1982), i.e., the I-129 is not controlling on the design of the repository. Scientific Committee: Leo K. Bustad, Chairman (1973-1981) Steven A. Book R. John Garner Joseph K. Soldat Fred P. Brauer, Consultant Leo L. Burger, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 074 - Biological Effects of Ultrasound: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications (1983) Price: $60 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Ultrasound is a very widely used modality in medicine, both therapeutically and diagnostically. Today, most infants in the US have been subjected to ultrasound examination in utero. Consequently, the biological effects of such exposures, if there are any, are of considerable importance. The present Report covers the basic physics of ultrasound with an emphasis on medical ultrasound fields. Treated are physical mechanisms for biological effects, the effects of ultrasound on plant, animal, human and in vitro systems. The Report provides recommendations for clinical safety and identifies research needs. Regarding human exposure, the Report specifically addresses applications of ultrasound in the areas of medical diagnosis, dentistry, physical therapy, surgery and hyperthermia. This Report is considered to represent a thorough coverage of the biological effects of ultrasound with special attention to clinical applications. As such, it is intended to be a valuable resource for health professionals and others involved with or interested in the use of ultrasound. NCRP is pleased to acknowledge the help of the Bioeffects and Standards Committees of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine (AIUM), whose members provided critical review of the Report at various stages of its preparation. AIUM is a Collaborating Organization of NCRP. Scientific Committee: Wesley L. Nyborg, Chairman Paul L. Carson Floyd Dunn Douglas L. Miller Morton W. Miller Marvin C. Ziskin Edward L. Carstensen, Advisor Horace E. Thompson, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 073 - Protection In Nuclear Medicine And Ultrasound Diagnostic Procedures In Children (1983) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The use of nuclear medicine and ultrasound in pediatric patients has undergone rapid growth in recent years. As in other branches of the radiological sciences, nuclear medicine practice should minimize radiation dose and, consequently, possible biological damage, provided that necessary information desired from the procedure is not diminished. As no significant biological effects from ultrasound diagnostic studies in pediatric patients have been reported, the implications of use must be treated in a more theoretical context. This Report considers the special problems of radiation protection and the biological effects of radiation associated with pediatric nuclear medicine and the biological implications from studies using ultrasound in pediatric patients. Pediatric patients are affected by different diseases from adults and respond in a different manner to illness. Similarly, the implications of any imposed biological burden are different from those in adult patients. NCRP Report No. 68 has considered the biological effects of conventional radiographic studies in pediatric patients (NCRP, 1981). Nuclear medicine and ultrasound equipment will be considered in general terms with special emphasis on specific application to the pediatric patient. The report includes a section devoted to the estimation of radiation dose, from a selected group of commonly used radionuclides, as derived from several pediatric phantoms. This Report also presents an appendix with an extensive tabulation of mean doses per cumulative activity (S values). Scientific Committee: A. Everette James, Jr., Chairman Glenn V. Dalrymple David L. Gilday James G. Kereiakes John W. Poston Eugene L. Saenger Michael M. Ter-Pogossian Robert W. Miller, Advisor |
 |
Report No. 072 - Radiation Protection and Measurements for Low Voltage Neutron Generators (1983) Price: $35 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 72 is concerned with neutron generators that operate at voltages below a few hundred kilovolts and produce neutrons chiefly by the T(d,n) reaction. The Report provides information on the radiation protection problems in the use of these generators and the means available for dealing with these problems. It is intended to serve as a guide to good practice and bring together in one place, a number of recommendations relevant to the use of low voltage neutron generators that have appeared in other NCRP documents. The Report surveys the radiations produced by low voltage neutron generators and their measurement. It then addresses the fundamentals of radiation protection, including shielding and physical safeguards. Guidance is given on radioactive waste resulting from the use of neutron generators and information is provided on nonradiation hazards and licensing. Appendices provide definitions of terms and treat the measurement of tritium and D-T neutron shielding. Scientific Committee: William C. Roesch, Chairman William S. Lyon, Jr. Peter Wooton |
 |
Report No. 070 - Nuclear Medicine - Factors Influencing the Choice and Use of Radionuclides in Diagnosis and Therapy (1982) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 70 offers broad guidance to those using radionuclides for medical purposes. This Report addresses the many factors which influence the choice of the proper radio pharmaceutical drug product for the diagnosis or treatment of a specific disease or condition. The Report examines decision-making considerations in the choice of radiopharmaceutical drug products and factors relevant to the choice of instruments utilized in nuclear medicine procedures. Important parts of the Report treat radiation dose and the evaluation of radionuclide procedures in their clinical utility. The Report also includes guidelines for performing nuclear medicine procedures. One appendix sets out the guidelines for clinical evaluation of radiopharmaceutical drugs developed by the Food and Drug Administration's Radiopharmaceutical Advisory Committee. Another appendix contains estimates of absorbed dose known for radiopharmaceutical drug products. Scientific Committee: A. Bertrand Brill, Chairman Ten expert members and consultants. |
 |
Report No. 069 - Dosimetry of X-Ray and Gamma-Ray Beams for Radiation Therapy in the Energy Range 10 keV to 50 MeV (1981) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 69 describes a dosimetric process that will allow the delivery of a prescribed absorbed dose from x-ray and gamma-ray sources to a uniform phantom within the accuracy needed for radiation therapy. The radiations considered in the Report are x rays with peak energies in the range from 10 keV to 50 MeV and gamma-rays from radionuclide therapy units. The Report describes and discusses the many recommended procedural details for the continuing proper delivery of absorbed dose by radiation therapy machines. The Report also considers the salient features of exposure and absorbed dose measurement that relate them to the national radiation standards, and includes a discussion of the uncertainty in the delivery of the absorbed dose. This Report addresses the rationale, the care and use of instruments, and the measurements required for radiation therapy machines. Discussion is limited to a single treatment field and a water or tissue phantom. Major sections of the Report cover basic parameters of photon beams and principles of dosimetry, national radiation standards, secondary standards, field instruments, commission, calibration and other measurements on radiation therapy machines, and uncertainty in delivery of absorbed dose. The Report also includes an appendix setting out definitions of terms relevant to dosimetry for radiation therapy. Scientific Committee: Robert J. Shalek, Chairman Ten expert members and consultants. |
 |
Report No. 068 - Radiation Protection In Pediatric Radiology (1978) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The purpose of this report is to make available a source of practical information regarding the manner in which radiologic examinations in children should be conducted to reduce the radiation dose to these patients and those responsible for their care. The emphasis is on radiologic examinations as they affect children, although some additional material of more general interest is included for completeness. The report. is mainly for the use of pediatricians, radiologists, radiologic technologists, and other physicians and medical practitioners who order or use radiological methods in examining children. It is recognized that there are many approaches to the reduction of dose in the radiologic examination of children. The guidelines in this report are intended as assistance in the reduction of unnecessary radiation exposure and should not be construed as specific regulations. Scientific Committee: Andrew K. Poznanski, Chairman Scott Dunbar Herman Grossman John A. Kirkpatrick William McSweeney Lester Weiss |
 |
Report No. 067 - Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields - Properties, Quantities and Units, Biophysical Interaction, and Measurements (1981) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 67 represents the first result of the Council's decision of some years ago to enter the area of nonionizing radiation. The initial objective stemming from that decision was the development of a report on quantities and units and on measurement techniques. Subsequently, biological effects and exposure criteria were to be examined. NCRP Report No. 67 is concerned with the first objective, although the Report represents an expansion of the effort to include material on properties and biophysical interactions of radiofrequency electromagnetic fields. Inclusion of these subjects permits a unified treatment of background material which is expected to be useful in the preparation of a subsequent report treating biological effects and exposure criteria. Report No. 67 is intended to be a comprehensive discussion of fundamentals, especially those that relate to radiation protection. In addition, it develops a perspective for those quantities and units that are needed to relate, quantitatively, a biological effect to a particular exposure. The Report represents, for nonionizing radiation, a step toward the goal, long sought in connection with ionizing radiation, of instilling increasing rigor into the definitions of fundamental quantities and units. It also represents a move toward the development of common nomenclature for the ionizing and nonionizing fields. In addition to definitions of quantities and units, the Report treats electromagnetic wave propagation, energy transfer processes, interaction of microwave with objects in the field, and measurement techniques. Appendices cover the natural background of nonionizing radiation in the biosphere and various aspects of energy absorption. Radiation in the biosphere and various espects of enrgy obsorption. Scientific Committee: George M. Wilkening, Chairman Frank S. Barnes Ronald R. Bowman Arthur W. Guy Karl H. Illinger Curtis C. Johnson (deceased) Saul W. Rosenthal Charles Susskind Ronald C. Peterson, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 065 - Management of Persons Accidentally Contaminated with Radionuclides (1980) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Report No. 65 results from recognition of the fact that the increasing use of radionuclides in research, medical applications, nuclear power, and industrial processes suggests that there is also a concomitant increase in the probability of accidental human exposures to internally deposited radionuclides. The review carried out during the preparation of the new Report made evident the fact that the literature on the medical management of such cases is scattered and sparse. Any individual physician or health physicist probably will have had experience with only a limited number of radionuclides and a limited variety of exposure conditions. Furthermore, the therapeutic effectiveness of some treatments has been tested only in animals. Other therapies may be thought to be useful but have not been evaluated for a particular radionuclide or accident situation. This Report is a collection of many of the data and ideas pertinent to accidental contamination into one document intended to aid those called upon to manage contaminated persons. An important part of the Report is a "quick reference section," written in such a way that useful advice can be rapidly obtained by consulting the tables set out in the section. In addition, the Report includes sections on initial management of the patient, diagnostic techniques to measure radioactive contamination, conceptual basis for treatment decisions, resume of experience with important radionuclides, and therapy procedures and drugs. Scientific Committee: George L. Voelz, Chairman H. David Bruner Thomas A. Lincoln Victor H. Smith Herta Spencer Niel Wald John W. Healy, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 064 - Influence of Dose and Its Distribution in Time on Dose-Response Relationships for Low-LET Radiations (1980) Price: $50 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The aim of this Report is to assess the genetic and carcinogenic effects of exposure in man to low doses of low-LET radiation, and to high doses delivered either at low-dose rates or in small increments protracted in time. Such effects may be expected in theory and on a statistical basis to occur at doses and dose rates well below those that cause acute effects. The assessment of the effects is then used to examine the validity of estimating the risk to man by interpolation from levels of effects observed at high doses and dose rates, on the assumption of a linear no-threshold dose-response relationship. Scientific Committee: Arthur C. Upton, Chairman (1972-1977) Victor P. Bond, Chairman (1977-1980) Fourteen expert members and consultants |
 |
Report No. 063 - Tritium and Other Radionuclide Labeled Organic Compounds Incorporated in Genetic Material (1979) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report addresses special hazards that might arise from the temporary or permanent incorporation of various radionuclides into the genetic material of the cell. NCRP was originally concerned with the question: "Does incorporation of tritium labeled thymidine directly into the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of synthesizing cells introduce complications that make the values of maximum permissible concentration (MPC) given in NCRP Report No. 22 (NCRP, 1959) inappropriate for this special case?" As the Council began to study this question, it became apparent that a broader consideration of various compounds labeled with several different radionuclides would be useful. The Council concluded that the use of various types of labeled compounds does introduce complications that do indeed make the use of certain values given in NCRP Report No. 22 inappropriate. Scientific Committee: Eugene P. Cronkite, Chairman Ten expert members. |
 |
Report No. 062 - Tritium in the Environment (1979) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Tritium, the heaviest and only radioactive isotope of hydrogen, is increasing in importance in energy and environmental considerations. This radionuclide is widely distributed throughout man's environment because of its ubiquitous form as tritiated water and its persistence in the environment. This Report considers and evaluates the available information on tritium in terms of its physical properties, production sources, physical transport, biological behavior, projected future production, waste management, and the long-term dose implications of tritium in the environment. Scientific Committee: Merril Eisenbud Thirteen expert members and consultants. |
 |
Report No. 061 - Radiation Safety Training Criteria for Industrial Radiography (1979) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report is concerned with the training of industrial radiographers and is devoted principally to those aspects of training that will provide the means to minimixe radiation exposure of human beings. The Report is intended as a guide for training persons in the safe use of sources of radiation for industrial radiography. The Report should be applied with sound judgment to formulate a training program that is responsive to particular needs. Important considerations that should be reviewed in formulating an appropriate and responsible training program include management practices, the equipment to be used, and applicable regulatory requirements. Provision should be made for continuing training in both a refresher and an updating fashion. Continuing education joined with increasing experience provides the proper foundation for optimizing worker performance with respect to both productivity and safety. Scientific Committee: Frank L. Paschal, Jr., (Chairman) Harry D. Richardson Robert B. Socky Paul L. Ziemer |
 |
Report No. 060 - Physical, Chemical, and Biological Properties of Radiocerium Relevant to Radiation Protection Guidelines (1978) Price: $40 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports Cerium, an element in the lanthanide series, has a number of radioactive isotopes. Several of these are produced in abundance in nuclear fission reactions associated with nuclear industry operations or detonation of nuclear devices. This report summarizes our present knowledge of the relevant physical, chemical, and biological properties of radiocerium as a basis for establishing radiation protection guidelines. Scientific Committee: Roger O. McClellan, Chairman Thirteen expert members from academia, government agencies and the private sector. |
 |
Report No. 058 - A Handbook of Radioactivity Measurements Procedures, 2nd edition (1985) Price: $90 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report addresses the measurement of radioactivity in general, but specifically it deals with the vast number of different radioactive materials that have become available in the last three decades, from nuclear reactors and particle accelerators, for applications in medicine, scientific research, and industry. It also addresses low-level radioactivity measurements for the monitoring of radioactivity in environmental media, such as air and water, in connection with the control of radioactive effluents associated with the production of nuclear power or the use of radionuclides. Scientific Committee: Wilfrid B. Mann, Chairman (deceased) Twenty two expert members and consultants. |
 |
Report No. 057 - Instrumentation and Monitoring Methods for Radiation Protection (1978) Price: $45 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports NCRP has made recommendations for the protection of individuals who may be exposed to radiation occupationally, or otherwise. To implement the recommendations, it is necessary to examine the radiation environment of persons, to evaluate the factors determining the likelihood of their exposure, and to estimate the actual exposure. It is the object of this Report to describe methods and instrumentation currently available for these purposes. The techniques, instruments, and practices described are applicable to all types of institutions concerned with radiation or radioactive materials. These institutions include industrial plants, scientific laboratories, universities, and hospitals or clinics. The radiation sources considered include x-ray machines, sealed and unsealed radioactive materials, low-energy accelerators, and low-power nuclear reactors. Additional and more elaborate instrumentation and measurement programs may be necessary and appropriate for specialized installations which may have unique problems beyond the scope of this Report. Scientific Committee: Arthur R. Keene, Chairman (1960 - 1967) Edward W. Webster, Chairman (1968 - 1978) Margarete Ehrlich John S. Handloser Jack S. Krohmer Richard T. Mooney Jacques Ovadia William C. Roesch |
 |
Report No. 055 - Protection of the Thyroid Gland in the Event of Releases of Radioiodine (1977) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report considers the feasibility of utilizing thyroid blocking agents, as an additional option, for protection of the public in case of off-site releases. NCRP does not take any position concerning the question of utilizing thyroid blocking agents in any given situation. Rather, the purpose of this Report is to define the efficacy of such agents and the contraindications for their use, and, hence, the potential for use of thyroid blocking agents. In view of concern about the possibility of large releases of radioiodine from nuclear reactors, the use of evacuation to mitigate the consequences of such a relew ia also discussed in this Report. Scientific Committee: Eugene L. Saenger, Chairman Eight expert members. |
 |
Report No. 054 - Medical Radiation Exposure of Pregnant and Potentially Pregnant Women (1977) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports It can be stated that no radiologic examination should be carried out unless there is a significant medical need for such examination at that time. It may also be stated that no radiological examination for which there is a significant medical need should be denied a patient, even if she is pregnant, for the risk to the patient of not having an indicated examination is also an indirect health risk to the embryo-fetus. However, there may be exceptions to this general thesis. The need for radiological examinations covers the entire spectrum of necessity, and health practitioners may, and often do, disagree as to the importance of a given examination in a given situation. There is presumably a radiation dose level below which most experts would agree that the risk of any radiation injury from a radiological examination (such as a routine chest x ray) is so small that it would be offset by any slight medical benefit. There is also a level, presumably, above which the risk of the radiological procedure is so great that it should not be carried out except to counteract a life-threatening situation (such as the radiation treatment of cancer). Individual experts will differ if asked to numerically define these levels, and they may draw different conclusions in trying to compare the risks with the benefits in a given situation because both are so often nonquantifiable or at least illdefined. NCRP recognizes that any general recommendation it makes regarding the medical radiation exposure of women having child-bearing capacity can serve only as a guide that may be modified in specific instances according to the judgment of the patient's physician and the consulting expert. Scientific Committee: Robert O. Gorson, Chairman Robert L. Brent Robert D. Moseley, Jr., Liane B. Russell James Wilson George W. Casarett, Consultant Lauriston S. Taylor, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 052 - Cesium-137 From the Environment to Man: Metabolism and Dose (1977) Price: $55 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report first outlines the environmental deposition of Cs-137 as fallout from atmospheric nuclear testing. The intent was not to document what has been found, but rather to draw from that experience the information that might be helpful in assessing the relative importance of various food chain pathways and in providing a broad understanding of the metabolism of Cs-137 in man. Second, dosimetry was explored rather fully, to give not only an average dose to the total body but also some idea of the departures from the average that might be expected. In particular, it appears that children, pregnant women, and some persons suffering from certain diseases eliminate cesium more rapidly than does the normal adult, and thus, receive less dose for a given contamination level in the diet. Maximum permissible concentrations (MPC), or equivalently maximum permissible annual intakes (MPAI), of Cs-137 are derived for occupational exposure to soluble compounds. No widespread use of insoluble compounds is known at this time. Fortunately, the wide availability of in vivo counters makes it feasible to follow directly such cases as might occur. While many critical points remain unanswered from the animal experimentation, a moderately large body of information has been accumulated on animals. The most significantt experiments are reviewed in Section 5. Scientific Committee: John C. Bugher, Chairman (1966-1970) - deceased Walter S. Snyder, Chairman (1970-1977) Eight expert members. |
 |
Report No. 050 - Environmental Radiation Measurements (1976) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report presents information on the properties of widelydistributed radionuclides and of typical radiation fields in the environment (Section 2), and on methods for their measurement (Sections 4-6). Emphasis is placed on the role of measurements in the realistic assessment of dose to man (see especially Section 3). Techniques applicable to routine monitoring programs during normal operation of nuclear facilities are described. Evaluations are made throughout the Report of the available and developing measurement methods. Areas are identified where present knowledge is limited due to the lack of adequate measurement capabilities or systematic data collection and appraisal (Section 7). The special requirements for monitoring abnormal occurrences such as large releases of radionuclides and for occupational radiation protection are not considered. Scientific Committee: James E. McLaughlin, Chairman Ten expert members and consultants. |
 |
Report No. 049 - Structural Shielding Design and Evaluation for Medical Use of X Rays and Gamma Rays of Energies up to 10 MeV (1976) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report supersedes NCRP Report No. 34, and is concerned with structural shielding design and evaluation for medical installations utilizing x rays and gamma rays of energies up to 10 MeV. The report contains recommendations and technical information as well as a discussion of the various factors which must be considered in the selection of appropriate shielding materials and in the calculation of the barrier thickness. Recent availability of new data used to calculate the shielding requirements has resulted in revision of some of the shielding requirement tables set out in Appendix C. Specific values of the parameters used in the formulation of the tables are explicitly given. The calculational procedures are presented in such a manner as to facilitate their use in deriving customized shielding requirements not to be found in the tables. An adjunct to the report presenting full sized reproductions of the curves for barrier requirements is also an innovation for the NCRP. This report is mainly intended for radiological physicists, radiologists, and regulatory personnel who specialize in radiation protecbon. Sections of the report should be of interest also to architects, hospital administrators, and others who are concerned with the planning of new radiation facilities. Scientific Committee: John P. Kelley, Chairman Robert O. Gorson Antolin Raventos David Keasey, Consultant Raymon Wu, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 047 - Tritium Measurement Techniques (1976) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports In the short time since the radioactivity of tritium was discovered by Alvarez and Cornog (1939), this radionuclide has become important in many scientific and industrial fields. Tritium occurs naturally and is also produced by nuclear fission and neutron activation. The incidental production of tritium in weapons tests and by the nuclear industry and the effects of tritium on man have received considerable attention (Jacobs, 1968). New uses of tritium in research and industry and expansion of the nuclear power industry seem certain. All of these activities encourage interest in tritium measurements. This Report describes and discusses methods for the measurement of tritium in a variety of media. It is intended to assist individuals and organizations in the selection of procedures best suited to particular problems and resources. Included are most of the important methods for the measurement of tritium and information on their advantages and disadvantages. Step-by-step procedures and detailed descriptions of equipment are beyond the scope of the Report, and the reader is advised to refer to the extensive literature cited to obtain this information. Scientific Committee: William C. Reinig, Chairman J.M. Robin Hutchinson John J. Koranda A. Alan Moghissi Robert V. Osborne H. Gote Ostlund John I. Peterson, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 046 - Alpha-Emitting Particles in Lungs (1975) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The potential for release of particles of plutonium and transplutonium alpha-emitting elements from nuclear power generating facilities poses urgent questions concerning spatial distribution of dose and the resultant biological effects. These questions &re of special importance in the setting of standards for radiation exposure. The major problems, and the pertinent information bearing on them, have been summarized in several recent compendia (ICRP, 1969; NCRP, 1971; ICRP, 1972; Hodge, et al., 1973; Bair, 1974; Bair and Thompson, 1974; Bair, et al., 1974; Tamplin and Cochran, 1974). We make no attempt, here, to review the general problem, but focus our attention on the specific problem of the biological effects of alpha-emitting particles in the lung. We address the question of whether the current practice of averaging over the lung the absorbed dose from particulate alpha-emitting radionuclides is a defensible procedure in the practice of radiation protection and whether exposure limits derived on this basis are more or less conservative than those that might result from a precise consideration of the spatial distribution of dose. Scientific Committee: William J. Bair, Chairman Albrecht Kellerer J. Newell Stannard Roy C. Thompson |
 |
Report No. 044 - Krypton-85 in the Atmosphere - Accumulation, Biological, Significance, and Control Technology (1975) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The projected rapid growth of the nuclear power industry necessitates a careful assessment of any related potential for environmental pollution. Kr-85 releases deserve special attention because of the inherent difficulty in their control and their essentially nonreactive and mobile nature in the atmosphere. The purpose of the present Report is to estimate the future global concentrations of Kr-85, their potential significance, and possible techniques for their control. Projections of Kr-85 accumulations will be made to the year 2000, as this is now sufficiently close to permit reasonable approximations to be made of the world's energy requirements and the extent to which they will then be fulfilled by nuclear power reactors. On the other hand, the year 2000 is sufficiently far off to allow for periodic reappraisal of the projections of Kr-85 accumulation in relation to developing information about the biological effects of this radionuclide and the technology for control of Kr-85 releases. In addition to the global projections, the present Report also includes estimates of Kr-85 concentrations near nuclear fuel chemical reprocessing plants. Scientific Committee: Merril Eisenbud, Chairman Ten expert members and consultants. |
 |
Report No. 042 - Radiological Factors Affecting Decision-Making in a Nuclear Attack (1974) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report was prepared to assist in preparedness activities for large disasters in which exposure of many people to nuclear radiation is of primary concern. In particular, those officially responsible for civilian preparedness against nuclear attack should find this report a basic resource for their task. It is an attempt to describe the important characteristics of radiation, with emphasis on radioactive fallout, and radiation injury so that they can be understood by people who will be responsible for decision-making in civil defense ope&ions in a nuclear attack. The recommendatiom must be regarded as reflecting the NCRP's best effort to evaluate information presently available; they may be modified as more knowledge becomes available. Scientific Committee: G.V. Leroy, Chairman (1968-70) G.W. Cassarett, Chairman (1970-74) E.L. Alpen J.L. Bateman H.A. Blair J. T. Brennan R. J. Hasterlik C. C. Lushbaugh J. H. Rust J.C. Greene, Consultant |
 |
Report No. 041 - Specification of Gamma-Ray Brachytherapy Sources (1974) Price: $25 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This Report is concerned with the spccification of sealed sources of nuclides which emit gamma rays-sources useful in brachytherapy. The Report resulted from the Council's belief that a single well-defined method for specifying the radionuclide in an encapsulated source would be advantageous for both the users and the suppliers of such sources. Presently, encapsulated radionuclides are being specified in terms of the activity of the radionuclide, in terms of the equivalent mass of radium, or in terms of the exposure rate at a specified distance from the source. This Report examines each of these methods of specification and, on the basis of this examination, develops recommendations on the method of specification considered to be appropriate. Although the subject matter presented in this Report is related to that found in NCRP Report No. 40, Protection Against Radiation From Brachytherapy Sources, this Report's content is limited to the characteristics of the sources themselves rather than to a discussion of the way in which they may and should be used. Scientific Committee: Marvin M. D. Williams, Chairman Ivan M. Grotenhuis Antolin Raventos Robert J. Shalek |
 |
Report No. 040 - Protection Against Radiation From Brachytherapy Sources (1972) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports This NCRP Report is concerned with the safe utilization of sealed radioactive sources in brachytherapy. Scientific Committee: E. L. Saenger, Chairman |
 |
Report No. 038 - Protection Against Neutron Radiation (1971) Price: $30 PDF (AAPM Members FREE) Category: Reports The present report was prepared by the Council's Scientific Committee 4 on Heavy Particles (Neutrons, Protons and Heavier). Scientific Committee: H. H. Rossi, Chairman 10 members and consultants |



















